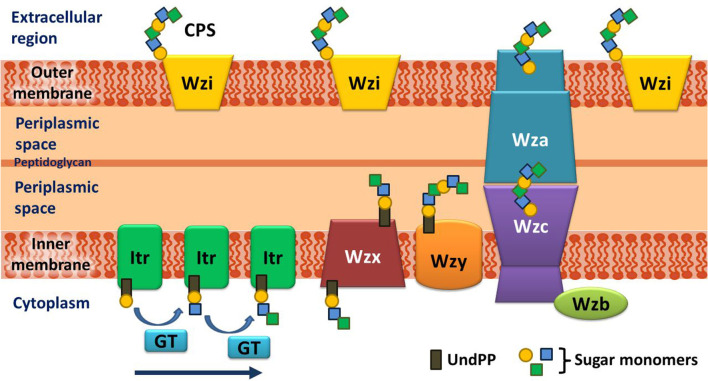
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the assembly and export of capsular polysaccharide (CPS) in A. baumannii. The assembly of the repeating unit begins with the transfer of the lipid carrier attached to the first sugar (Und-PP) to the initializing transferase (Itr) located in the inner membrane. Subsequently, the other sugar monomers of the repeating unit are added (indicated by an arrow) by K-type specific glycosyltransferases (GTs) on the cytosolic side of the inner membrane. The CPS repeating unit is, then, transported to the periplasmic region through the Wzx flippase that is located on the inner membrane. The CPS repeating unit is polymerized by the Wzy protein and exported to the cell surface synergistically by Wzc (tyrosine autokinase), Wzb (phosphatase), and Wza (translocon). It is noteworthy that the Wzi protein, which plays a crucial role in retaining the integrity of the CPS layer on the exterior of the outer membrane, is present in a different locus and not in the cps locus of A. baumannii (doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-01206-5), unlike in Klebsiella (doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2019.00367) and E. coli (doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00070).