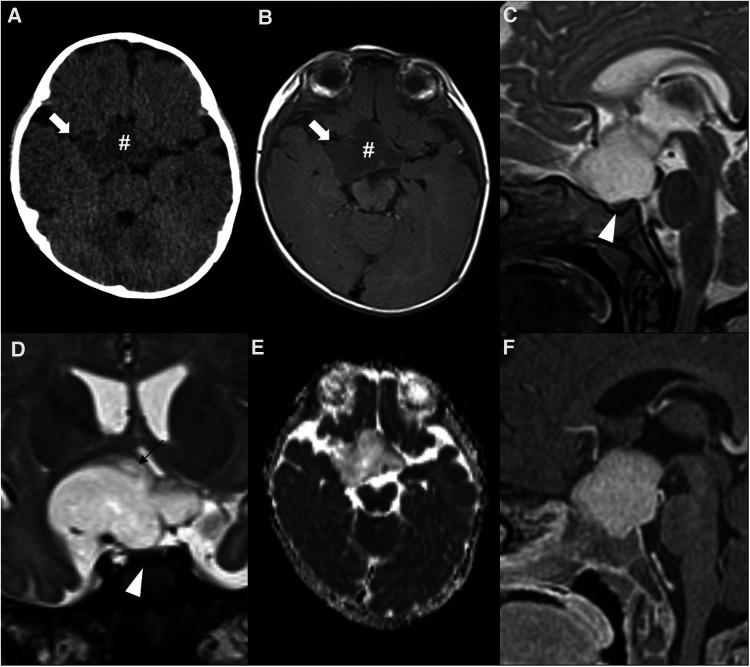
Figure 11.
Sporadic hypothalamic and optic pathway astrocytoma in a 7-month-old girl presenting with horizontal nystagmus. Axial head CT (A) and axial brain MRI T1WI (B) shows a hypodense and hypointense expansile lesion (hashtags) centered in the suprasellar region, with extension towards the sylvian fissures, mainly on the right (white arrows). Sagittal (C) and coronal (D) T2WI show a T2 hyperintense lesion which is separated from the pituitary gland (white arrowheads) and originating posterior from the optic chiasm, most probably from the right hypothalamus (black arrow in D). The chiasm and optic tracts (right optic tract is pointed out by the black arrowhead in D) are splayed but not overtly infiltrated. There are no optic nerve changes (not shown). Facilitated diffusion is seen on ADC map (E), as well as homogeneous contrast enhancement on sagittal T1WI after gadolinium injection (F).