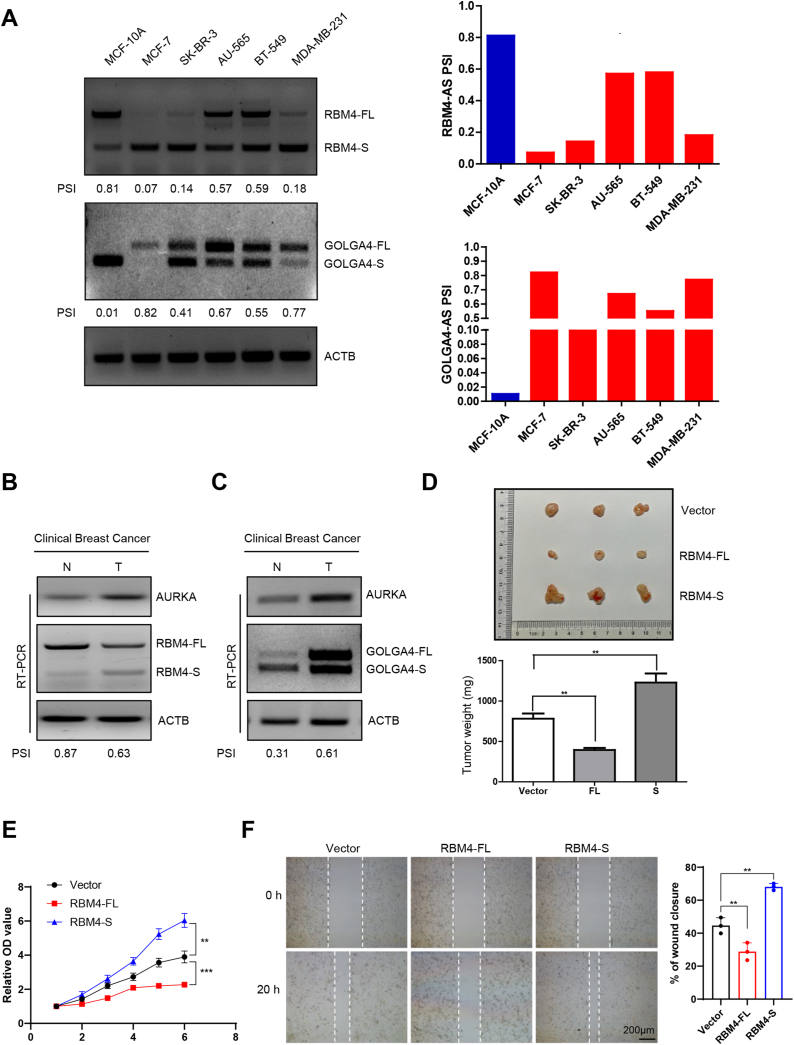
Fig. 2.
Aberrant splicing of RBM4 and GOLGA4 is closely related to breast cancer development. (A) Relative mRNA abundance of RBM4, and GOLGA4 splicing in MCF-10A and other breast cancer cell lines was examined by RT-PCR. (B–C) Validation of RBM4 and GOLGA4 splicing switch in clinical breast cancer specimens by RT-PCR. N, normal; T, tumor. (D) Immunodeficient mice were subcutaneously inoculated with equal numbers of MDA-MB-231-vector, RBM4-FL, and RBM4-S cells (2 × 106 cells per mouse, n = 3). Photograph of tumors and tumor weights are shown. (E) MDA-MB-231 cells were stably transfected with vector, RBM4-FL, RBM4-S plasmids, and the proliferative ability of cells was analyzed by cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) assay. (F) The migration ability of cells was analyzed by wound healing assay. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. P values were calculated with the two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.