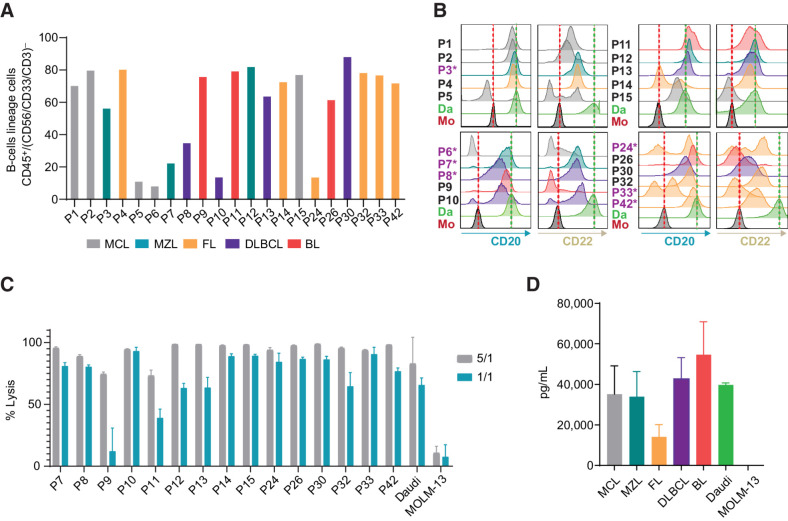
Figure 5.
CD20xCD22 CAR T cells efficiently target primary B-NHL cells. A, Graph showing percentage of cells from the B-lineage identified in B-NHL primary samples, defined by %CD45+ cells within CD56−/CD33−/CD3 (N = 21). B, Flow cytometry data representing the level of CD20 and CD22 expression in samples from A. Patients previously treated with rituximab are indicated with an asterisk (N = 21). C, CD20xCD22 CAR T-cell cytotoxic activity against B-NHL samples. D, IFNγ release upon exposure to primary B-NHL cells to CD20xCD22 CAR T cells.