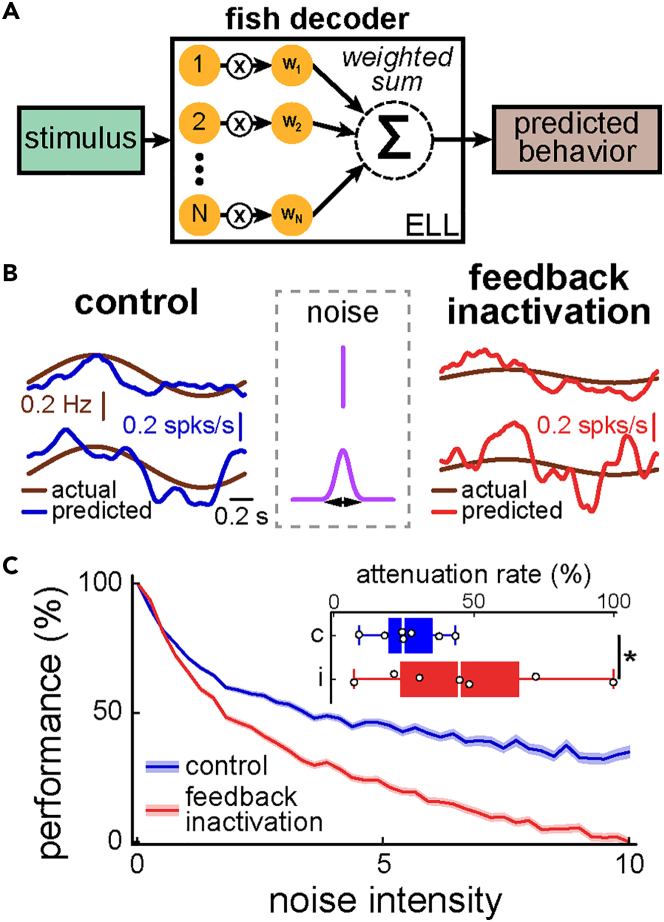
Figure 4.
Downstream decoders take advantage of the beneficial function of heterogeneities to generate behavior
(A) Schematic showing decoding. Neural responses to the envelope are weighted and the weights are chosen such as to minimize the mean-squared error between the weighted sum of neural activities (i.e., the predicted behavior) and the actual behavior.
(B) Actual (brown) and predicted behavioral responses before (blue, top left) and after (red, top right) feedback inactivation. To test decoding robustness, independent normally distributed random numbers (i.e., noise) was added to each weight and the standard deviation of the distribution was progressively increased (see middle column). Increasing noise intensity increased the error between predicted and actual stimulus waveforms to a lesser extent before (blue, bottom left) than after (red, bottom right) feedback inactivation.
(C) Performance as a function of noise intensity before (blue) and after (red) feedback inactivation. It is seen that performance is more greatly attenuated after feedback inactivation. Inset: The rate of increase of performance attenuation was greater after feedback inactivation. (Wilcoxon signed rank test; p = 0.016, N = 7).