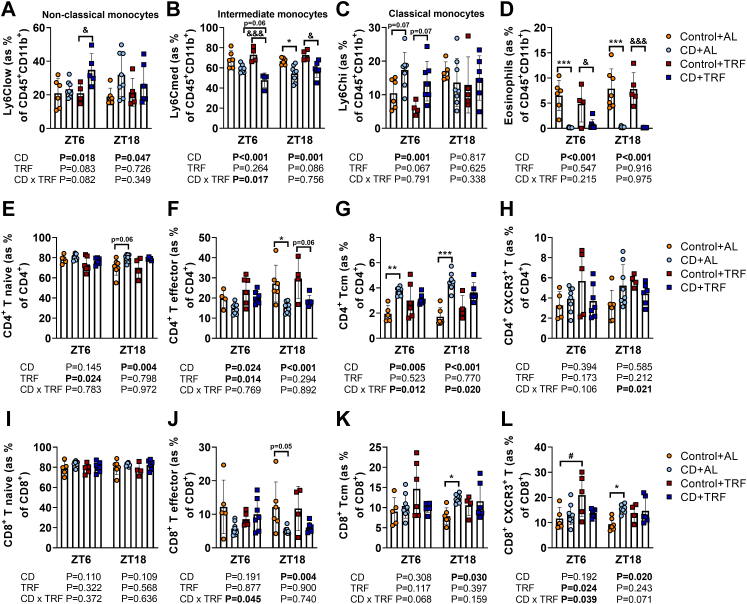
Fig. 4.
Circulating monocytes, eosinophils, and T cells. APOE∗3-Leiden.CETP mice were exposed to 6-h phase advancement every 3 days (circadian disturbance; CD) or regular 12:12 light–dark cycle (Control), while having either ad libitum food access (AL) or food access during the dark phase only (time-restricted feeding; TRF) for a total duration of 14 weeks. During days 94–95, blood was collected to measure abundance of circulating (A) non-classical monocytes (Ly6Clow), (B) intermediate monocytes (Ly6Cmed), (C) classical monocytes (Ly6Chigh), (D) eosinophils, (E) cluster of differentiation (CD)4+ T naive cells, (F) CD4+ T effector cells, (G) CD4+ T central memory (Tcm) cells, (H) CD4+ C-X-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 3 (CXCR3+) T cells, (I) CD8+ T naive cells, (J) CD8+ T effector cells, (K) CD8+ Tcm cells, and (L) CD8+ CXCR3+ T cells using flow cytometry (n = 4–8 mice/group/time point). Data are presented as means ± SD. #Control + AL vs. Control + TRF; ∗ Control + AL vs. CD + AL; &Control + TRF vs. CD + TRF. #,∗,& P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗,&&& P < 0.001, according to two-way ANOVA and following Tukey's multiple-comparison test.