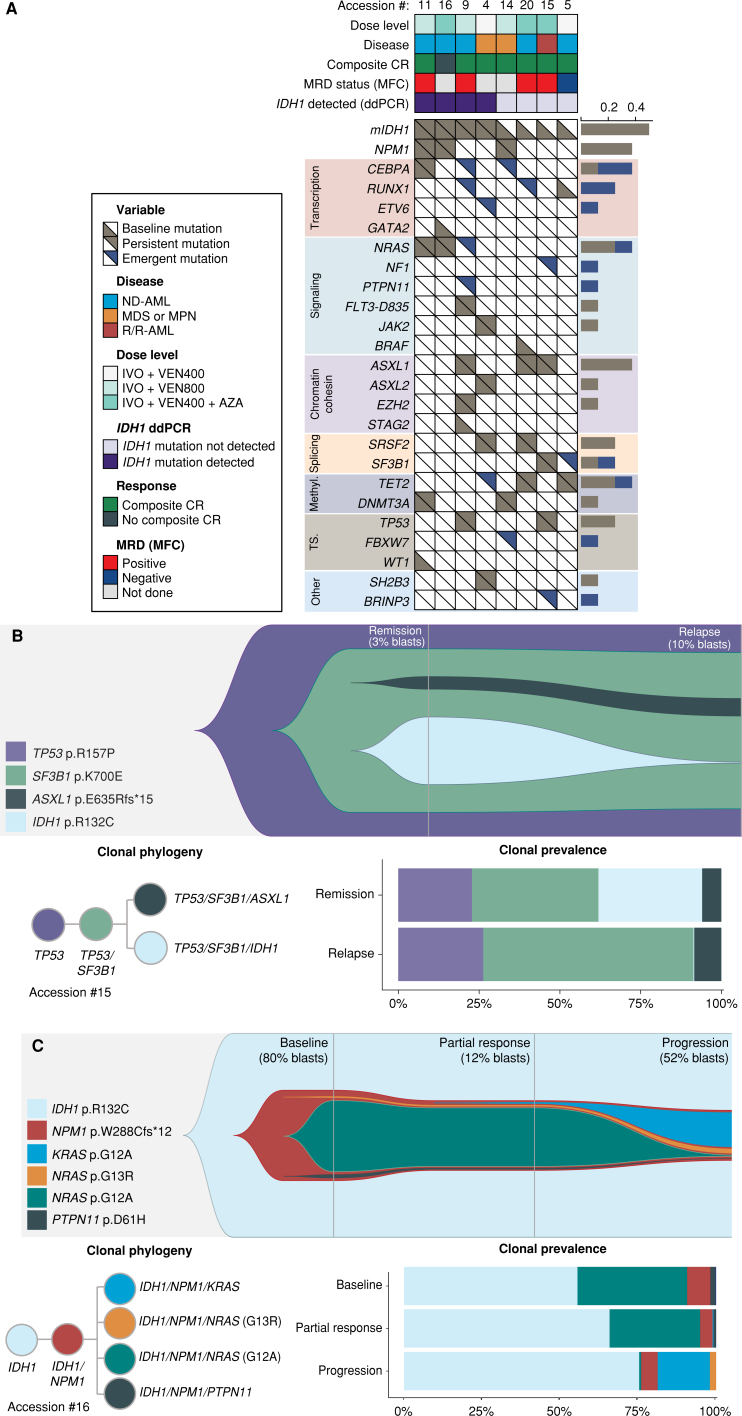
Figure 3.
Bulk NGS and single-cell correlates of relapse in patients treated with IVO + VEN ± AZA. A, Bulk next-generation myeloid gene panel sequencing at the time of diagnosis and at relapse in responding patients treated with IVO + VEN or IVO + VEN + AZA who ultimately relapsed following treatment. B, scDNA-seq in a patient with R/R-AML (Accession #15) at the time of remission and relapse identified expanding leukemic clones contributing to relapse. C, scDNA-seq in a patient with ND-AML (Accession #16) demonstrating differing clonal architecture with respect to signaling mutations and variants throughout treatment. Methyl., methylation; T.S., tumor suppressor.