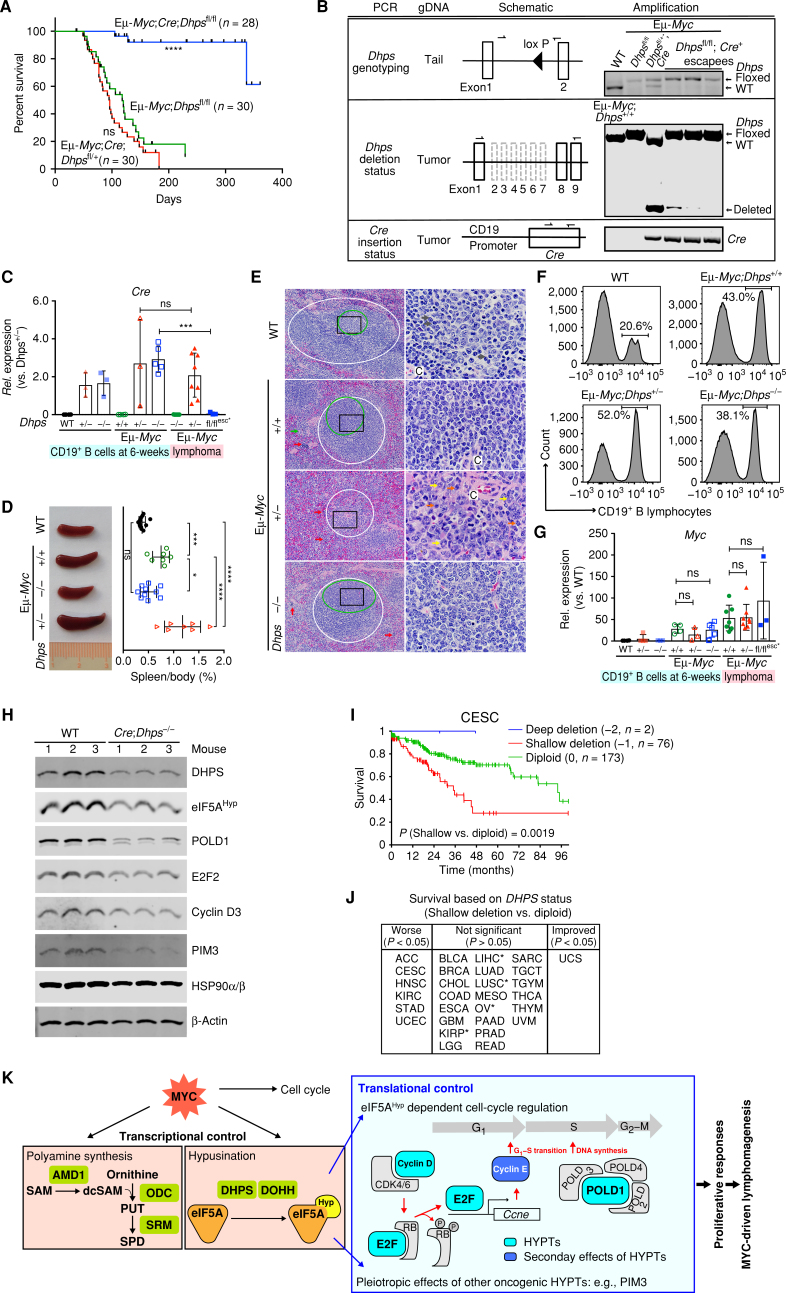
Figure 7.
Dhps is essential for the development of MYC-driven lymphoma. A, Kaplan–Meier curves showing survival of Eμ-Myc;CD19-Cre;Dhpsfl/fl, Eμ-Myc;CD19-Cre;Dhpsfl/+, and Eμ-Myc;Dhpsfl/fl mice. B,Dhps deletion and Cre knock-in status, as determined by genomic PCR of the indicated tissues or tumor samples. C,Cre expression in CD19+ B cells from 6-week-old WT, CD19-Cre;Dhpsfl/+ (hereafter Dhps+/−), and CD19-Cre;Dhpsfl/fl (Dhps−/−); and from preneoplastic and malignant Eμ-Myc;CD19-Cre;Dhps cohorts (Eμ-Myc;Dhps+/+, Eμ-Myc;Dhps+/−, and Eμ-Myc;Dhps−/−) and the 3 Cre escapees (fl/flesc*), as determined by qRT-PCR (n ≥ 3 mice). Fold change was calculated relative to Cre levels in Dhps± B cells. D, Left, representative images; right, the weight of spleens (normalized to total body weight) from indicated 6-week-old mice (n > 7 for each cohort). E, Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of spleens from indicated 7-week-old mice. Periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths (PALS) and germinal centers are shown in white and green circles, respectively. Red, green, yellow, gray, and blue arrows indicate erythroid precursors, megakaryocytes, maturing granulocytic precursors, small lymphocytes, and large lymphocytes, respectively. Central arteriole is indicated as C. Black box in the left panels shows the area magnified in the right panels; scale bars, left and right, 50 μm and 10 μm, respectively. F, Representative CD19+ B-cell profiles of BM-derived lymphocytes of indicated 6-week-old mice. G,Myc expression in CD19+ B lymphocytes from indicated 6-week-old littermates, and from preneoplastic and malignant Eμ-Myc;CD19-Cre;Dhps cohorts (+/+, +/−, and −/−; n ≥ 3). H, Immunoblot analyses of identified eIF5AHyp targets in CD19+ B lymphocytes from CD19-Cre;Dhpsfl/fl and WT littermates (n = 3). I, Kaplan–Meier curves showing survival of cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CESC) based on DHPS copy-number status. J, Overall survival based on DHPS copy number (shallow deletion vs. diploid). TCGA cancer types in the middle panel that are associated with trends toward worse survival are marked as * (P < 0.1). K, Model for roles of eIF5AHyp in MYC-driven lymphoma. The requirement for eIF5AHyp for Eμ-Myc B-cell growth and malignant conversion is associated with MYC-induced hyperactivation of the polyamine–hypusine circuit and eIF5AHyp-dependent translation of targets such as E2F and POLD1 (turquoise boxes). Cyclin E (blue box) is the transcription target of E2F. HYPTs, eIF5AHyp targets; PUT, putrescine; SPD, spermidine; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; dcSAM, decarboxy SAM. Levels of significance determined by Mantel–Cox log-rank test (A) and (I), unpaired t tests (C), or Dunnett multiple comparison (D) and (G) are indicated as follows: ns, not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Error bar indicates mean ± SD.