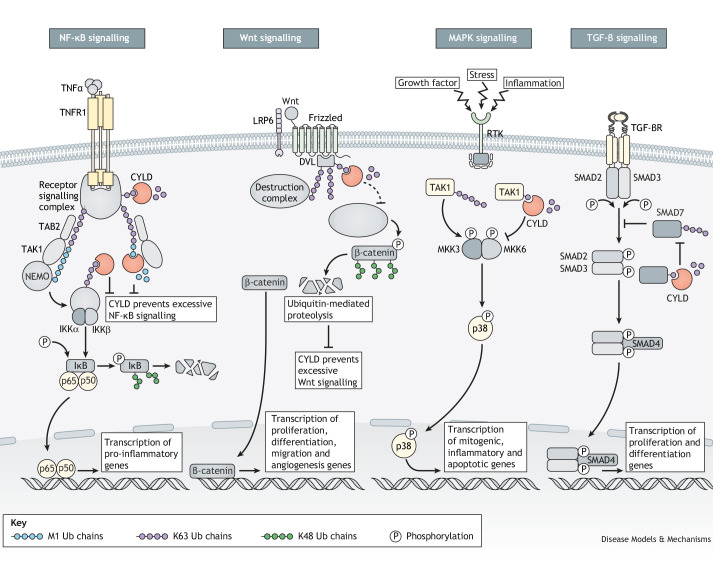
Fig. 3.
CYLD regulates cell signalling pathways through deubiquitination of effector proteins. CYLD regulates a range of signalling pathways through its deubiquitinase activity, targeting K63- and M1-linked polyubiquitin chains of effector proteins. CYLD represses NF-κB signalling by deubiquitinating receptor signalling complex proteins such as those associated with the TNFα receptor, as well as its downstream effectors such as TAB2. In Wnt signalling, CYLD deubiquitinates dishevelled (DVL) to prevent the sequestering of β-catenin, thereby reducing Wnt signal transduction. CYLD also affects regulation of MAPK signalling by targeting K63 polyubiquitination of TAK1 after receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) activation. Thereby, CYLD impedes p38-mediated gene transcription. Finally, CYLD promotes TGF-β signalling through deubiquitination of SMAD7, thereby preventing SMAD7-mediated inhibition of SMAD2/3 phosphorylation (P). K48 Ub, K48-linked ubiquitin; K63 Ub, K63-linked ubiquitin; M1 Ub, M1-linked ubiquitin.