Abstract
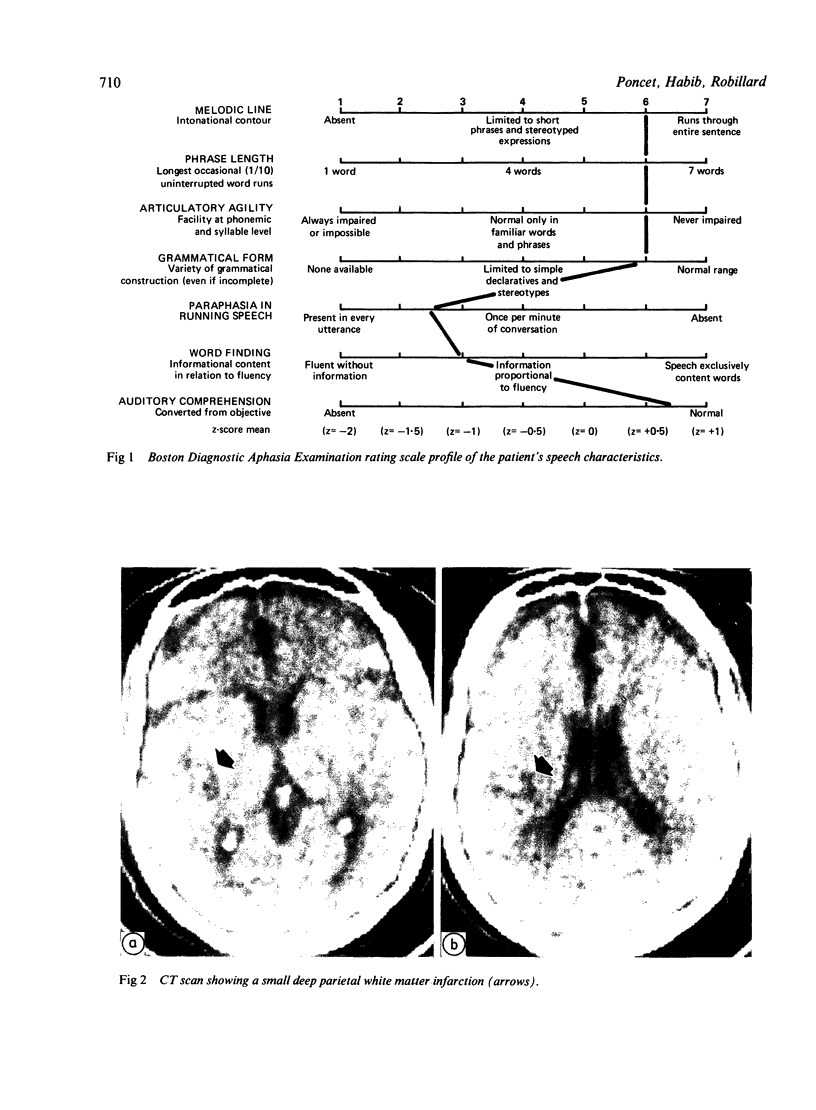
A patient with sudden onset of conduction aphasia in the context of an ischaemic stroke is reported. Other neurological and neuropsychological findings included bilateral ideomotor apraxia, right hemisensory defect and paradoxical left ear extinction on a dichotic listening test. Lesion location, as inferred from magnetic resonance imaging, involved a restricted subcortical area in the left parietal lobe, near the lateral wall of the cerebral ventricle. The anatomical correlate for each of the clinical findings is discussed in the light of classical anatomo-clinical correlations. It is concluded that this tetrad constitutes a specific syndrome which may be easily recognised and ascribed to a single lesion in the deep white matter of the left parietal lobe.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson D. F., Sheremata W. A., Bouchard R., Segarra J. M., Price D., Geschwind N. Conduction aphasia. A clinicopathological study. Arch Neurol. 1973 May;28(5):339–346. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490230075011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogousslavsky J., Assal G., Regli F. Aphasie afférente motrice et hémisyndrome sensitif droit. Le syndrome de l'artère pariétale antérieure gauche. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1982;138(8-9):649–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damasio H., Damasio A. R. The anatomical basis of conduction aphasia. Brain. 1980 Jun;103(2):337–350. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.2.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damasio H., Damasio A. "Paradoxic" ear extinction in dichotic listening: possible anatomic significance. Neurology. 1979 May;29(5):644–653. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.5.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER C. M. LACUNES: SMALL, DEEP CEREBRAL INFARCTS. Neurology. 1965 Aug;15:774–784. doi: 10.1212/wnl.15.8.774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER C. M. PURE SENSORY STROKE INVOLVING FACE, ARM, AND LEG. Neurology. 1965 Jan;15:76–80. doi: 10.1212/wnl.15.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. M. Thalamic pure sensory stroke: a pathologic study. Neurology. 1978 Nov;28(11):1141–1144. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.11.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geschwind N. Disconnexion syndromes in animals and man. I. Brain. 1965 Jun;88(2):237–294. doi: 10.1093/brain/88.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geschwind N. The apraxias: neural mechanisms of disorders of learned movement. Am Sci. 1975 Mar-Apr;63(2):188–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman K. M., Rothi L. J., Valenstein E. Two forms of ideomotor apraxia. Neurology. 1982 Apr;32(4):342–346. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.4.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria A. R., Hutton J. T. A modern assessment of the basic forms of aphasia. Brain Lang. 1977 Apr;4(2):129–151. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(77)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez M. F., Benson D. F. Atypical conduction aphasia. A disconnection syndrome. Arch Neurol. 1985 Sep;42(9):886–891. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060080068018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr J. P., Kase C. S., Meckler R. J., Fisher C. M. Sensorimotor stroke due to thalamocapsular ischemia. Arch Neurol. 1977 Dec;34(12):739–741. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1977.00500240027004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandya D. N., Hallett M., Kmukherjee S. K. Intra- and interhemispheric connections of the neocortical auditory system in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res. 1969 Jun;14(1):49–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks R., Goodglass H., Nickel B. Ipsilateral versus contralateral extinction in dichotic listening resulting from hemisphere lesions. Cortex. 1970 Sep;6(3):249–260. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(70)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lacoste M. C., Kirkpatrick J. B., Ross E. D. Topography of the human corpus callosum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1985 Nov;44(6):578–591. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198511000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]