FIGURE 7.
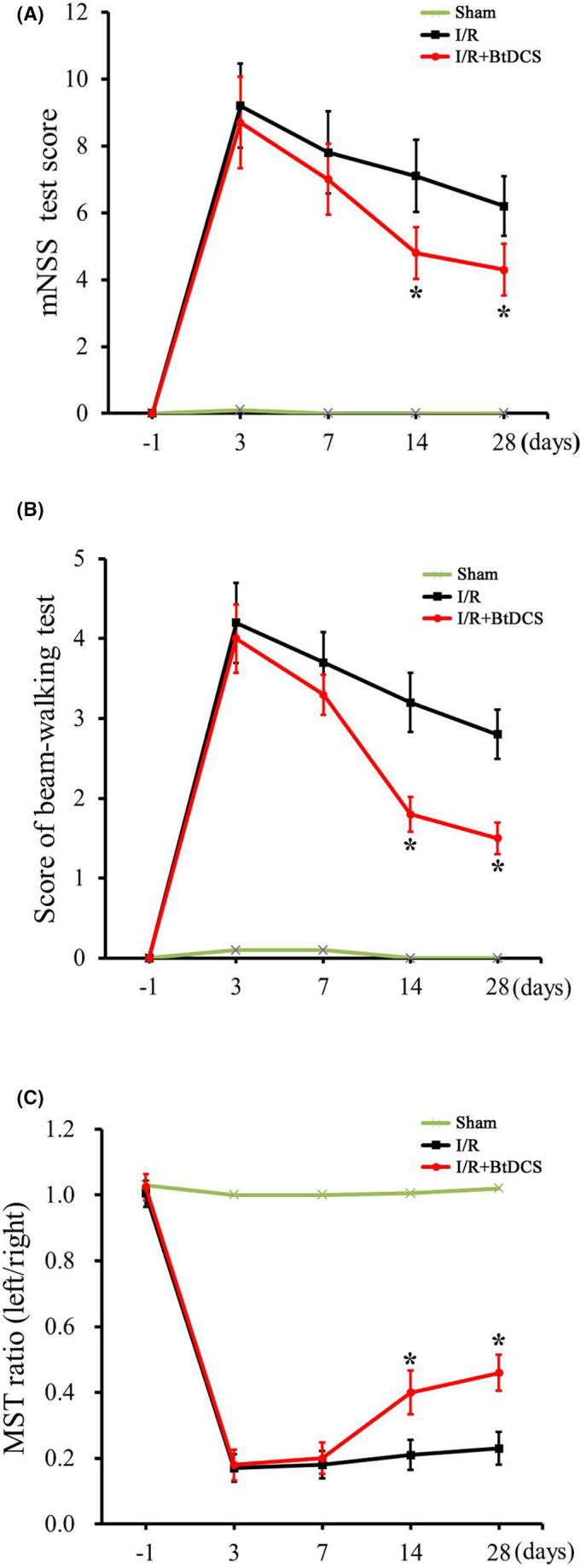
BtDCS improves the neurobehavioral function of stroke animals. (A) Summarized data show that rats treated with BtDCS for 150 μA for 30 min per day for 12 days have significantly lower scores of mNSS tests on day 14 (I/R group score = 7.2 ± 1.02; I/R + BtDCS score = 4.8 ± 0.77) and day 28 (I/R group score = 6.2 ± 0.85; I/R + BtDCS score = 4.0 ± 0.67) after MCAO, (n = 7 rats for each group, *p < 0.05 vs. I/R; ANOVA and subsequent post hoc Bonferroni's test). (B) Summarized data show that rats treated with BtDCS for 150 μA for 30 min per day for 12 days have significantly lower scores of beam‐walking test on day 14 (I/R group score = 3.2 ± 0.48; I/R + BtDCS score = 2.1 ± 0.35) and day 28 (I/R group score = 2.8 ± 0.43; I/R + BtDCS score = 1.7 ± 0.22) after MCAO, (n = 9 rats for each group, *p < 0.05 vs. I/R; ANOVA and subsequent post hoc Bonferroni's test). (C) Summarized data show that rats treated with BtDCS for 150 μA for 30 min per day for 12 days have a significantly higher ratio of a modified sticky tape test on day 14 (I/R group score = 0.21 ± 0.03; I/R + BtDCS score = 0.40 ± 0.06) and day 28 (I/R group score = 0.24 ± 0.03; I/R + BtDCS score = 0.46 ± 0.06) after MCAO (n = 7 rats for each group, *p < 0.05 vs. I/R; ANOVA and subsequent post hoc Bonferroni's test).
