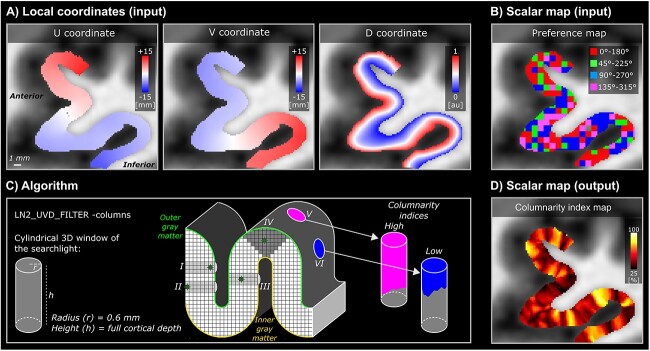
Fig. 3.
Overview of the searchlight algorithm for functional cortical column detection. A-B) Input examples of local coordinates (U, V, D) and BOLD preference map of left-hMT+ for one example participant (sub-01). C) Conceptualization of the algorithm on a toy model of a cortical ribbon. A searchlight with a cylindrical 3D window is evaluated at each voxel position. On the toy model, we show the searchlight (dark gray voxels with cardinal axes) and its relative 3D window (light gray). For every position of the searchlight, the window adapts to the geometry of the ribbon and covers the entire cortical depth (see examples (I) voxel close to the outer gray matter, (II) voxel close to the inner gray matter, (III) voxel close to the middle gray matter on a wall, (IV) voxel close to the middle gray matter on a gyrus). Pink cylinder is an example of a high columnarity index (V), whereas the blue cylinder is an example of a low columnarity index (VI). D) Output example of the columnarity index map generated for the data (B) of the same participant.