Figure 3.
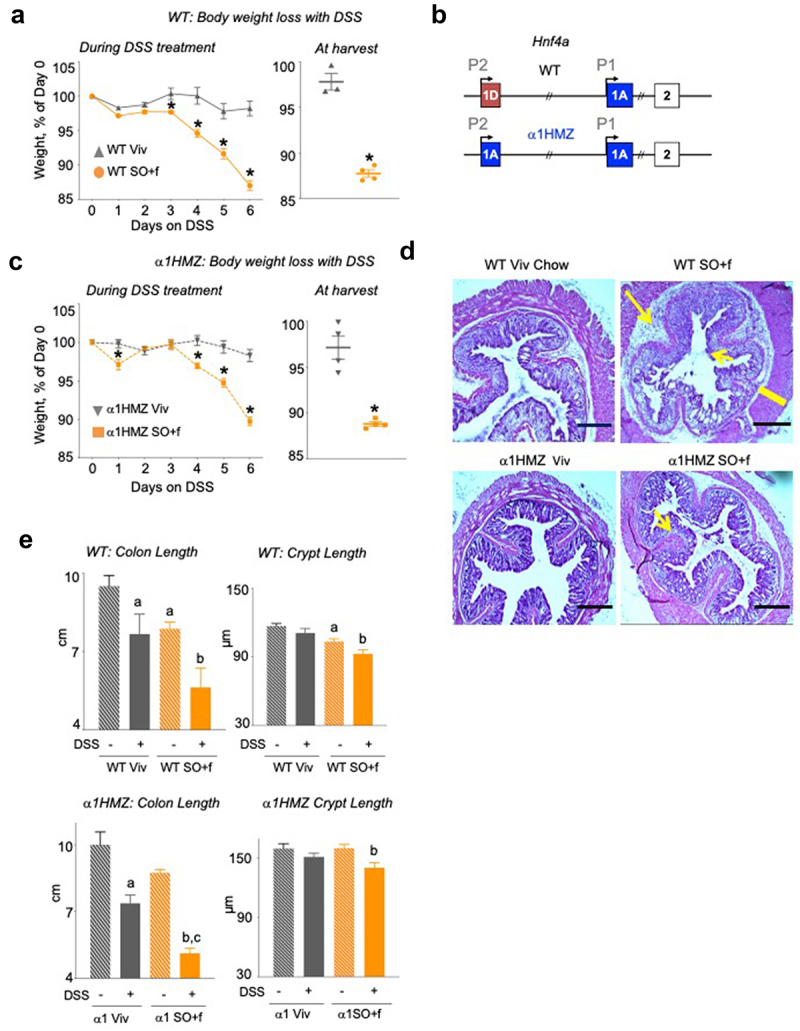
A diet high in LA increases colitis susceptibility and decreases barrier function in WT and α1HMZ mice.
Notes: (a) WT mice on Viv chow or SO+f diet for 15 weeks were treated with 2.5% DSS in their drinking water for 6 d: % weight loss of DSS-treated mice, body weight at harvest; the body weight at harvest is a few days after the last data point in the weekly body weight graph. * vs Viv P < .05, T-test N = 3–4 per group (b) Schematic of the mouse Hnf4a gene showing the two promoters (P1 and P2) (top), and the exon-swap (1D to 1A) that drives the expression of only P1-HNF4α in α1HMZ mice. α1HMZ mice on Viv chow or SO+f diet for 15 weeks were treated with 2.5% DSS for 6 d. (c) % body weight loss, weight at harvest, * vs α1HMZ Viv P < .05, T-test N = 3–4 per group. (d) Representative colonic histology. Big arrow, immune infiltrate; small arrow, loss of crypt structure; line, thickening of muscularis in SO+f. Scale bar is 400 microns. (e) Colon length and crypt length (at least 10 crypts were measured per mouse) Additional sections are shown in Supplementary Figures S2 and 3. a vs untreated WT, b vs untreated α1HMZ Viv, c vs untreated α1HMZ SO+f. One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc. N = 5–12 per group.
