Figure 5.
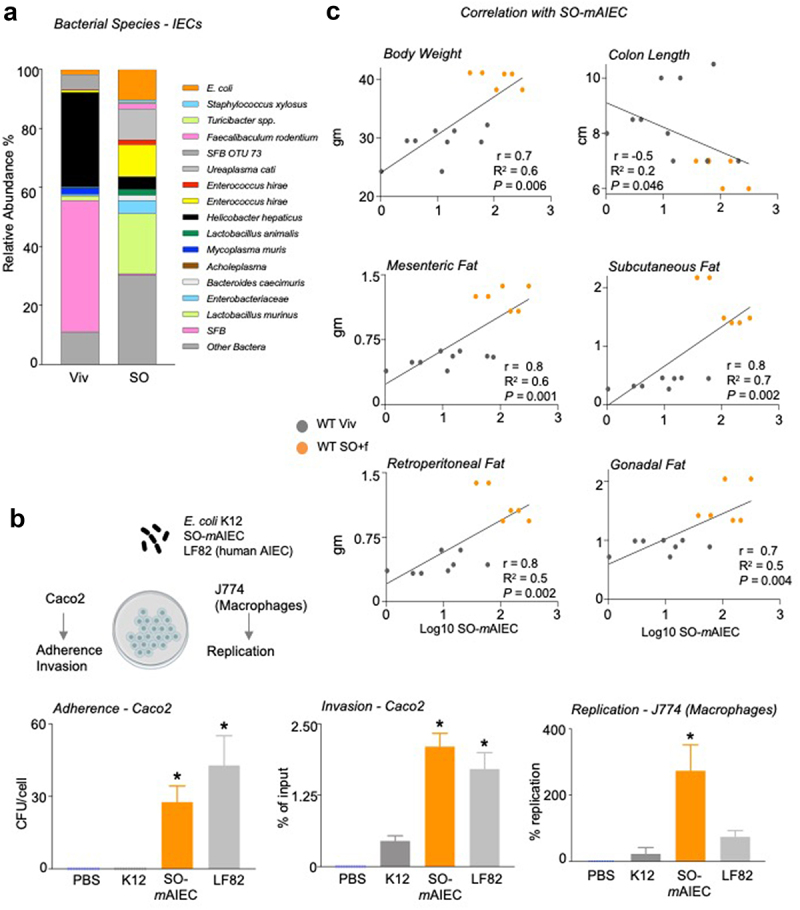
A diet high in LA increases the abundance of SO-mAIEC in WT mouse intestines.
Notes: (a) Bacterial species plots of intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) from the small and large intestines (N = 4–5) of mice fed Viv chow or an SO diet, with no added fiber. (b) Correlations between indicated mouse metadata and log10 of SO-mAIEC relative abundance in the IECs of mice fed Viv or SO+f diets. Spearman’s correlation coefficient (r) (for the body weight and adipose tissue) and Pearson correlation coefficient (for colon length) (r) goodness of fit or R2 values for linear regression and P value of the correlations (P) are indicated on the graphs. (c) Phenotypic characterization of the E. coli isolate enriched by SO (SO-mAIEC), compared with the human AIEC LF82 and the nonpathogenic E. coli K12. Assessments were made for bacterial adherence to Caco-2BBe cells, intracellular invasion of CaCo-2BBe cells, and replication in J774A.1 murine macrophages as indicated. * P < .05, one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post hoc comparison. N = 12 across four experiments.
