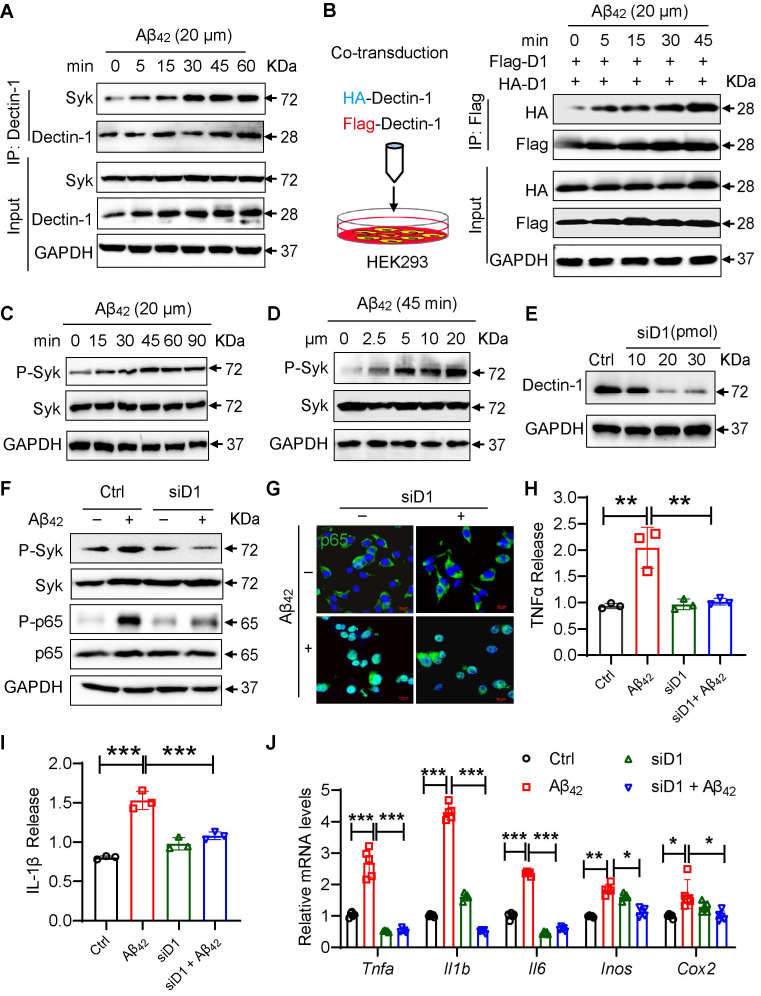
Figure 5.
Dectin-1 interference prevents Aβ42-induced inflammatory response in BV2 cells. (A) Time-course of Dectin-1-Syk interaction. BV2 cells were exposed to 20 µM Aβ42 for indicated times and co-immunoprecipitation using Dectin-1 antibody to probe for Syk was performed. (B) HEK-293T cells were transfected with Flag-tagged Dectin-1 (Flag-D1) and HA-tagged Dectin-1 (HA-D1). Time-course of Dectin-1 dimerization (Flag-HA interaction) assessed following exposure of cell to 20 µM Aβ42 for indicated times. (C) Time-course of Syk phosphorylation. BV2 cells are exposed to 20 µM Aβ42 for indicated times. Total proteins were extracted and probed for p-Syk and Syk levels. GAPDH was used as loading control. (D) Dose-course of Syk phosphorylation. BV2 cells were exposed to increasing levels of Aβ42 for 45 mins. Total proteins were used to measure p-Syk and Syk levels. GAPDH was used as loading control. (E) Determination of Dectin-1 interference efficiency in BV2 cells. Total proteins were extracted and probed for p-Syk and Syk levels. GAPDH was used as loading control. (F) Representative western blot analysis of p-Syk, Syk, P-NFκB65, and NFκB65 in BV2 cells. GAPDH was used as loading control. (G) Representative immunofluorescence staining of NFκB65 (green) in BV2 cells transfected with or without siD1 [scale bar = 10 μm]. (H) TNFα release in cell supernatant measured by ELISA. (I) IL-1β release in in cell supernatant measured by ELISA. (J) mRNA levels of Tnfa, Il1b, Il6, Inos, and Cox2 in the hippocampus tissues. Transcript levels were normalized to GAPDH.