Figure 1.
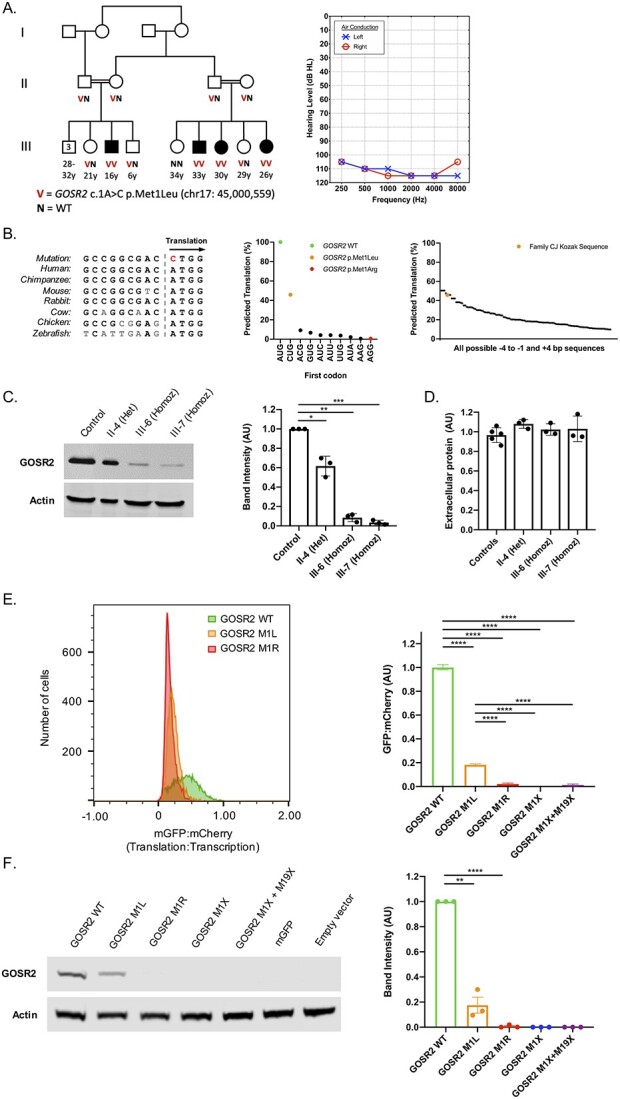
Clinical and cellular features of GOSR2 p.Met1Leu. (A) Family CJ with congenital non-syndromic sensorineural hearing loss in four children (filled symbols), with genotypes at GOSR2 c.1A>C, p.Met1Leu and an audiogram of III-3. (B) Nucleotide alignment of the GOSR2 Kozak sequence across multiple species (left), with predicted translation efficiency of human GOSR2 alternate start codons, given the GOSR2 Kozak sequence in family CJ [adapted from Ref. (3); center], and predicted translation efficiencies of CUG start codons with different surrounding Kozak sequences [adapted from Ref. (3); right]. (C) Western blot of GOSR2 in cultured lymphoblasts (LCLs) from members of family CJ and a control, with quantification of band intensities normalized to actin and to GOSR2 protein level of the control. (D) Total extracellular protein in culture media following 48 h incubation of LCLs from family members of homozygous and heterozygous GOSR2 genotypes and five controls; all P-values less than E – 10. (E) Translation:transcription ratios, indicated by monomeric green fluorescent protein:mCherry, for GOSR2 p.Met1Leu, p.Met1Arg, and reference; and cellular translation:transcription ratios, normalized to wild-type (see also Supplementary Material, Fig. S1). (F) Western blot of GOSR2 translation in transfected cells used in flow experiments, with quantification of GOSR2 band intensities, normalized to actin and to reference protein levels. Error bars indicate standard errors; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
