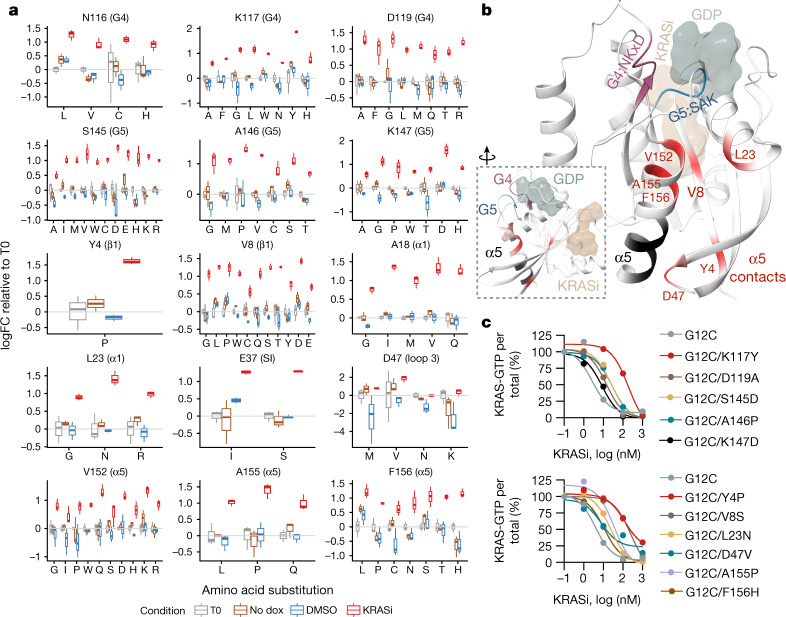
Fig. 3. Diverse allosteric effects on inactive state selective KRAS inhibition.
a, H358 cells were infected with a dox-inducible saturation mutagenesis library based on a KRAS G12C backbone and treated with either DMSO or KRASi for 2 weeks. The selection of mutations in amino acids far from drug-binding interface are shown (median, interquartile range and Tukey whiskers, n = 3). FC, fold change; T0, time 0. b, Residues from a were mapped in the cocrystal structure of KRAS G12C with the KRAS inhibitor. Residues involved in α5 contacts that were not identified in the screen are shown in black. Inset, 90° rotation. c, HEK293 cells expressing KRAS with a single G12C mutation or double mutants involving substitutions in the G4 and G5 motifs (top) or α5 helix contacts (bottom) were treated as shown for 2 h. Cell extracts were subjected to RBD pull down, immunoblotting and densitometry to determine the effect on KRAS-GTP concentrations. A representative of two independent repeats is shown in c.