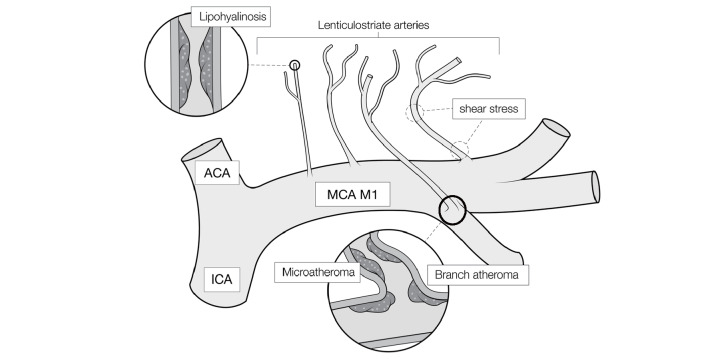
Fig.1. Schematic diagram of a perforating branch lesions of the middle cerebral artery causing the branch atheromatous disease (BAD) or lacunar infarction.
The branches of the lenticulostriate arteries (LSA) are thicker and steeply angled toward the outer side of M1 and run in the opposite direction of blood flow in M1, i.e., inward. These anatomical characteristics of LSA are based on the generation of microatheroma, leading to platelet activation by shear stress. Some LSAs may have lipohyalinosis, which causes lacunar infarction instead of BAD.
Solid circles, enlarged views of inside of the blood vessel
ACA, anterior cerebral artery; ICA, internal carotid artery; MCA M1, proximal segment of the middle cerebral artery