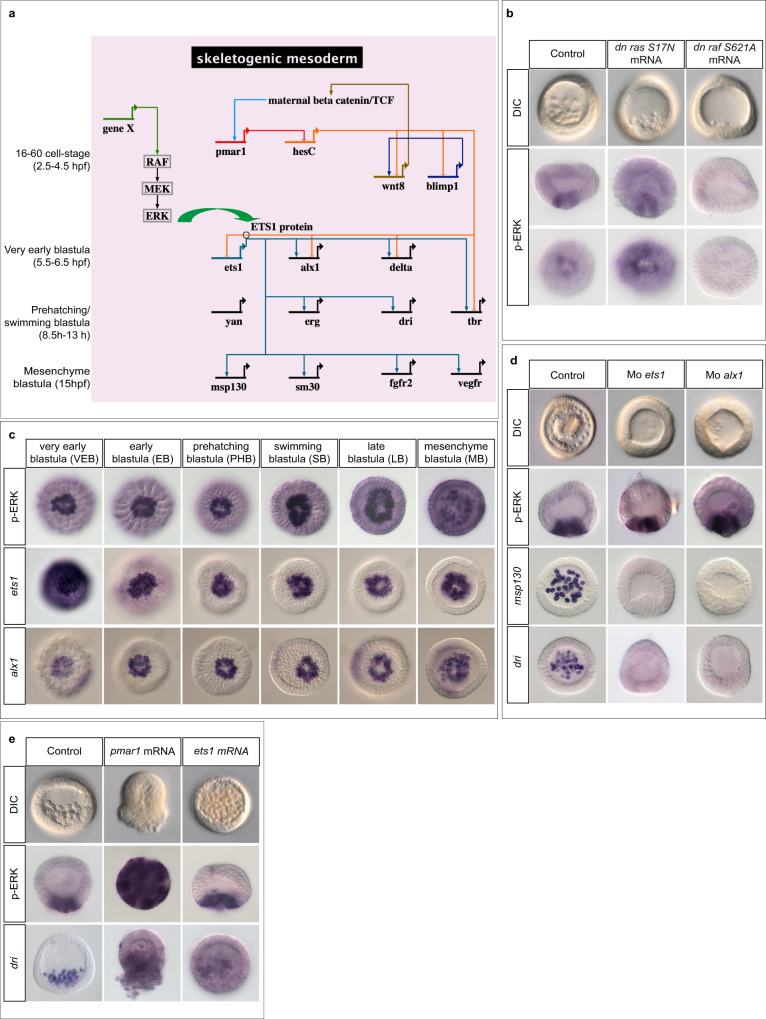
Fig. 1. The ERK pathway is activated early in the skeletogenic precursors downstream of pmar1 but independently of alx1 or ets1.
a Biotapestry82 diagram of the simplified gene regulatory network (GRN) driving specification and differentiation of the skeletogenic mesoderm in Paracentrotus lividus (see also14, 15, 20). A time scale is given from top to bottom on the left side. The GRN is activated by nuclearization of maternal beta-catenin in micromeres around the 16-cell stage. In the micromeres, beta-catenin triggers the expression of the homeobox gene pmar1. By repressing the expression of the ubiquitously expressed repressor of the PMC differentiation program, hesC, in the PMCs, Pmar1 allows the expression of regulatory genes further downstream in the GRN including wnt8, blimp1, ets1, alx1, erg, yan, tbr and dri in the skeletogenic mesoderm. Ets1 is a central regulator of this GRN and regulates the expression of two layers of genes encoding transcription factors including aristaless-like1 (alx1), tbrain (tbr), yan/tel, erg and dead ringer (dri)12, 13. Activation of the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway is crucial for the activity of Ets1 and for the expression of alx1 but the signals/genes responsible for activation of the pathway and their exact position in the GRN are not known (gene X). The green arrow depicts phosphorylation of Ets1 by ERK. b Activation of ERK in the PMC precursors occurs independently of RAS but requires RAF. c time-course of ERK activation and of ets1 and alx1 expression reveals that activation of ERK in the PMCs coincides with the onset of zygotic expression of ets1 and alx1 in these cells. The strong in situ hybridization signal for ets1 at very early blastula stage is due to maternal ets1 transcripts. Activation of ERK is detected by immunostaining with an antibody against the di-phosphorylated (activated) form of ERK. All the embryos in (c) are viewed from the vegetal pole. Note that at very early blastula stage, which corresponds to the beginning of ERK activation, only 50 % of the embryos show ERK activation in the PMC precursors while 100% of the embryos are labelled at later stages. d Morpholino mediated knock-down of ets1 or alx1 blocks delamination of the PMCs and suppresses expression of PMC marker genes msp130 and dead ringer (dri) but it does not inhibit activation of ERK in the PMCs. e although overexpression of either ets1 or pmar1 can trigger a massive EMT at blastula stage, only overexpression of pmar1 induces massive ectopic activation of ERK. The number of times the experiments were replicated and the number of embryos analyzed are indicated in See Supplementary Table 1.