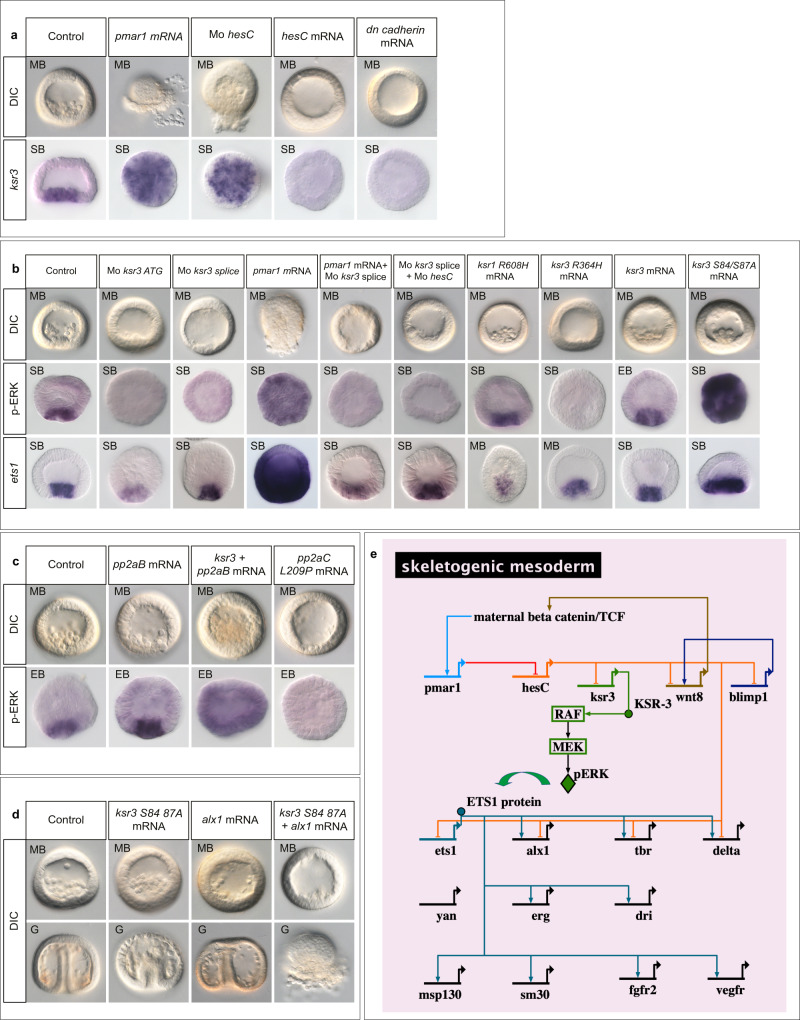
Fig. 4. KSR3 is required for activation of ERK in the PMCs and for the ability of Pmar1 to convert any cell of the embryo into PMCs.
a Expression of ksr3 is positively regulated by Pmar1 and repressed by HesC. Injection of pmar1 or injection of an antisense morpholino oligonucleotide targeting the hesC transcript caused a massive ectopic expression of ksr3 while overexpression of hesC mRNA abolished ksr3 expression. b Injection of antisense morpholino oligonucleotides targeting the ksr3 translation start site (Mo-ksr3ATG) or targeting the exon4-intron4 junction (Mo-ksr3 splice) prevented activation of ERK in the skeletogenic precursors. While overexpression of pmar1 induced a massive activation of ERK, co-injection of pmar1 mRNA and of ksr3 splice morpholino suppressed the pmar1-induced activation of ERK, resulting in embryos devoid of PMCs. Injection of the ksr3 splice morpholino also suppressed the massive EMT and activation of ERK caused by injection of a morpholino oligonucleotide targeting the HesC transcript. Injection of mRNA encoding a dimerization defective KSR1 factor (KSR1 R608H) did not block activation of ERK in the PMC precursors and did not perturb EMT of these cells. In contrast, injection of mRNA encoding a dimerization defective KSR3 factor (KSR3-R364H) caused the same phenotype as that caused by the ksr3 morpholinos, blocking activation of ERK and PMC delamination. Overexpression of ksr3 does not cause ectopic activation of ERK. However, substitution of alanine for serine 84 and serine 87 of KSR3 produced a constitutively active KSR3 factor that was able to ectopically activate ERK signalling in the embryo. EB early blastula, SB swimming blastula, MB mesenchyme blastula, G Gastrula, DIC Differential Interference Contrast. c Co-overexpression of ksr3 and of the regulatory subunit of PP2A induces massive activation of ERK while overexpression of a dominant negative form of the catalytic subunit of PP2A abrogates activation of ERK and EMT. d While single overexpression of the ERK pathway activator ksr3 or of the PMC specification gene alx1 do not cause any morphological phenotype, co-overexpression of alx1 and ksr3 induces a massive production of PMCs and a large wave of EMT at the vegetal pole. e Biotapestry82 diagram showing position of the genetic circuit responsible for activation of ERK signalling in the PMC gene regulatory network: ksr3 is a target of the Pmar1-HesC double negative gate. The number of times the experiments were replicated and the number of embryos analyzed are indicated in See Supplementary Table 1.