FIGURE 1.
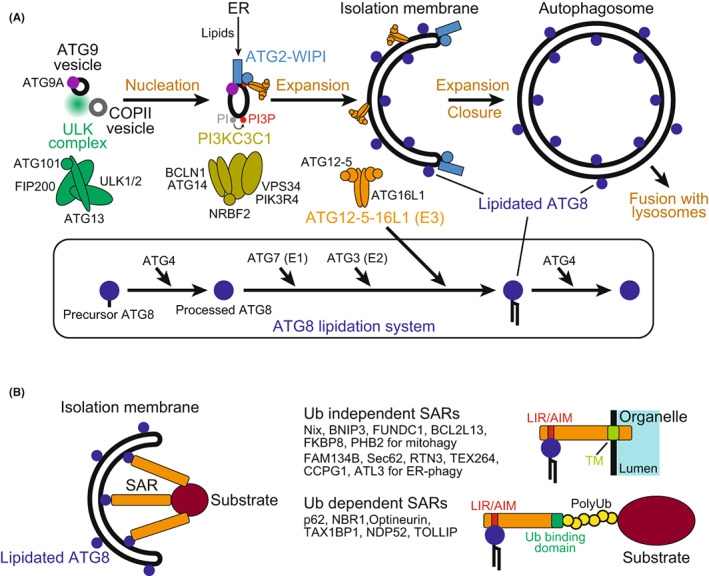
Basic mechanisms of autophagy. (A) Core autophagy machinery mediating autophagosome formation. The ULK complex initiates autophagy by promoting nucleation of isolation membranes. PI3KC3C1 produces PI3P and recruits ATG2–WIPI, which promotes the expansion of isolation membranes by transferring lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) with the help of ATG9A. ATG12–ATG5–ATG16L1 promotes ATG8 lipidation by functioning as the E3 enzyme, resulting in the decoration of isolation membranes with lipidated ATG8. (B) Basic mechanism of substrate recognition during selective autophagy. Selective substrates are tethered to isolation membranes via lipidated ATG8 and selective autophagy receptors (SARs), promoting their sequestration into autophagosomes. SARs are classified into two types. One is ubiquitin‐independent and directly recognizes substrates (often possessing transmembrane domains in the case of SARs for organelles) and the other is ubiquitin‐dependent and recognizes polyubiquitin chains attached to substrates. Both types possess LC3‐interacting region (LIR)/Atg8‐family interacting motif (AIM) to bind ATG8.
