FIGURE 2.
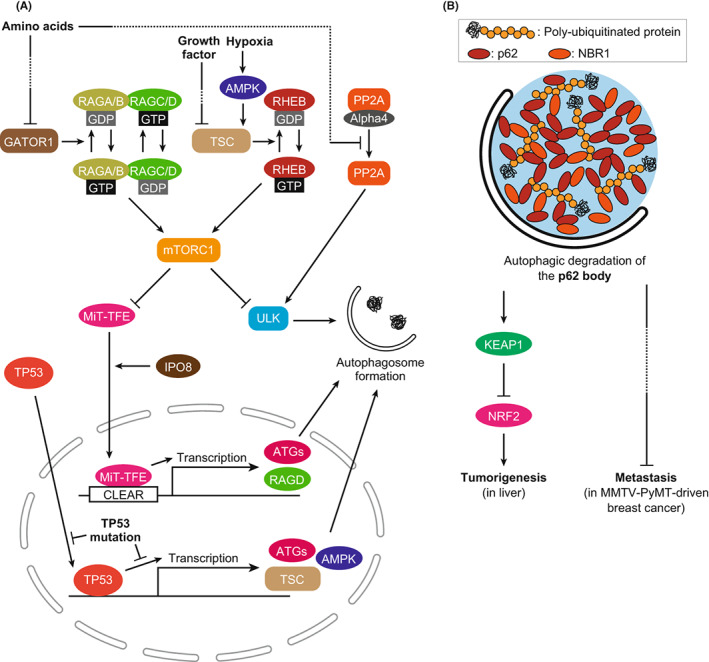
Autophagy and cancer. (A) Cancer‐associated regulation pathways of autophagic activity. The activity of mTORC1 is directly involved in the regulation of autophagy, and its activity is disrupted in many types of cancers. Independent of mTORC1, the PP2A complex regulates autophagy by dephosphorylating the ULK complex. Transcriptional regulation of autophagy by TP53 and MiT‐TFE family proteins is disrupted in cancer cells. (B) Role of autophagic degradation of the p62 body in cancer. The p62 body is an LLPS‐related structure containing polyubiquitinated proteins, p62, and NBR1. In autophagy‐deficient cells, the p62 body accumulates and may trigger cancer pathogenesis. In liver cells, accumulated p62 bodies sequestrate and inactivate KEAP1, leading to tumorigenesis through NRF2 activation. In MMTV‐PyMT–driven breast cancer, accumulated NBR1 in the p62 body induces metastasis via an unknown pathway.
