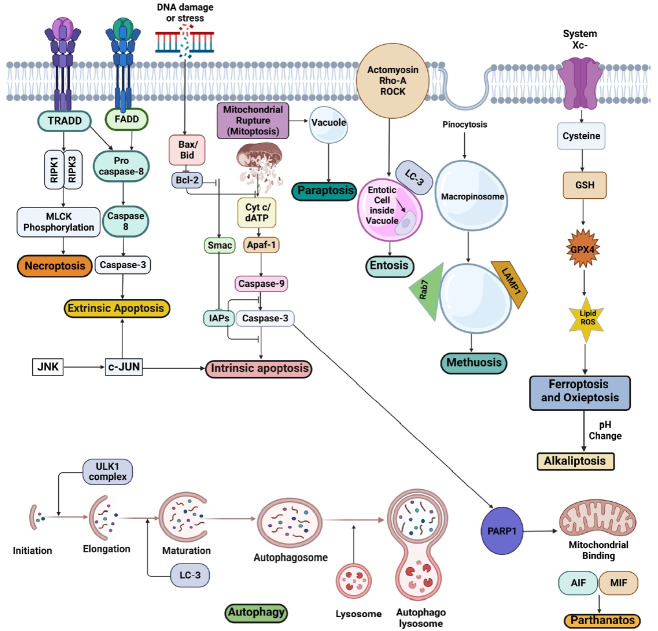
Fig. 3.
Essential pathways involved in cell death associated with spinal cord injury. This image illustrates different cell death pathways and their crosstalks (apoptosis, anoikis, autophagy, methuosis, entosis, paraptosis, parthanatos, mitoptosis, ferroptosis, NETosis, pyroptosis, necroptosis, oxieptosis, and alkaliptosis). Anoikis uses the same signaling pathways as apoptosis involving the membrane and mitochondrial disruption and activation on executioner caspase-3, except that poor or incorrect cell-matrix connections trigger it. This caspase 3 can also trigger mitochondrial rupture causing mitoptosis and PARP1 activation causing AIF and MIF to dimerize and translocate to trigger parthanatos. Autophagy basically involve ULK1 mediated autophagosome formation that one side can trigger cleaning of cellular debries at injury site and also promote inflammation by triggering cytokine production. Ferroptosis involves GPX4 activation by iron accumulation leading to pH change and ROS production possibly triggering oxieptosis and alkaliptosis. Necoptosis occours by MLCK phosphorylation induced necrosome formation. Cell death modes with unknown mechanisms were excluded. The arrow direction shows the causal relationship. TRADD, type 1-associated death domain protein; FADD, Fas-associated death domain protein; RIPK, receptor-interacting protein kinase; MLKL, mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bid, BH3 interacting-domain death agonist; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Cyt-c, cytochrome-c; Apaf-1, apoptotic protease activating factor-1; Smac, second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase; IAP, inhibitor of apoptosis; ULK1, Unc-51-like kinase 1; MOMP, mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization; AIF, apoptosis-inducing factor; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; PARP-1, poly-(ADP-ribose)-polymerase 1; LC3, microtubule-associated protein light chain 3; LAMP1, lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1; Rab-7, Ras-related protein-7; Rho-A, Ras homolog family member A; ROCK, Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase; GSH, glutathione; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; ROS, reactive oxygen species; JNK, Janus kinase; c-JUN, C-junctional protein.