Fig. 3.
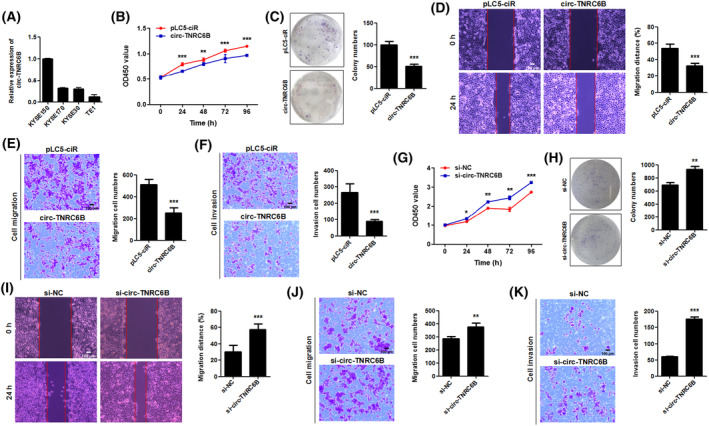
circ‐TNRC6B suppresses the proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities of ESCC cells. (A) The relative expression level of circ‐TNRC6B in four ESCC cell lines was examined by qRT‐PCR (n = 2). (B, C). The proliferative and clonogenic ability of TE1 cells after exogenous circ‐TNRC6B transfection was detected by CCK‐8 (n = 4, P‐values were determined by two‐way ANOVA) and colony formation assay (n = 3, P‐values were determined by Mann–Whitney U‐test). Data are represented as mean ± SD. (D, E) The migration ability of TE1 cells after exogenous circ‐TNRC6B transfection was detected by wound healing and transwell migration assay. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3, P‐values were determined by Mann–Whitney U‐test). Scale bar: 100 μm. (F) The invasion ability of TE1 cells after exogenous circ‐TNRC6B transfection was detected by transwell invasion assay. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3, P‐values were determined by Mann–Whitney U‐test). Scale bar: 100 μm. (G, H) The proliferative and clonogenic ability of KYSE150 cells after silencing circ‐TNRC6B expression was detected by CCK‐8 (n = 4, P‐values were determined by two‐way ANOVA) and colony formation assay (n = 3, P‐values were determined by Mann–Whitney U‐test). si‐NC: negative control of siRNA. (I, J) The migration ability of KYSE150 cells after silencing circ‐TNRC6B expression was detected by wound healing and transwell migration assay. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3, P‐values were determined by Mann–Whitney U‐test). Scale bar: 100 μm. (K) The invasion ability of KYSE150 cells after silencing circ‐TNRC6B expression was detected by transwell invasion assay. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3, P‐values were determined by Mann–Whitney U‐test). Scale bar: 100 μm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
