Fig. 4.
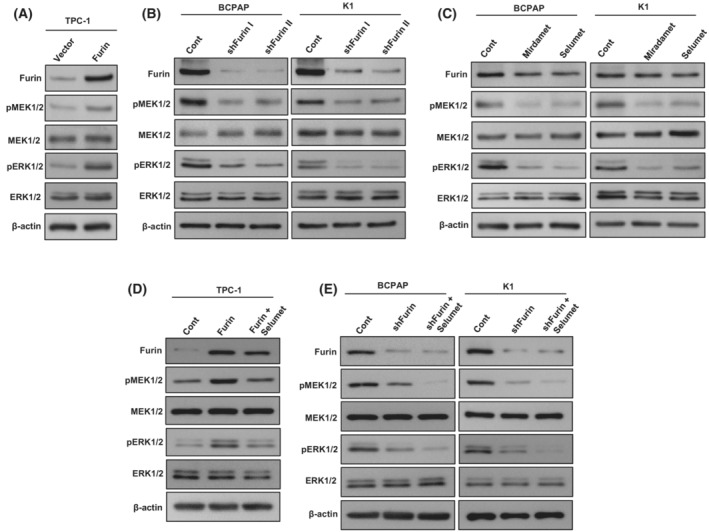
Furin activates MEK/ERK pathway. (A) Forced expression of furin stimulates MEK/ERK pathway. TPC‐1 cells were transfected with either an empty vector or FURIN cDNA for 48 h. Cells were lysed and proteins were immuno‐blotted with antibodies against Furin, pMEK1/2, MEK1/2, pERK1/2, ERK1/2, and β‐Actin as indicated (n = 3). (B) Depletion of furin inhibits MEK/ERK activation. PTC cells were transfected with a control shRNA vector or two different FURIN shRNA constructs. After transfection, cells were lysed and proteins were immuno‐blotted with antibodies against Furin, pMEK1/2, MEK1/2, pERK1/2, ERK1/2, and β‐Actin as indicated (n = 3). (C) The effect of MEK inhibitors on furin expression. PTC cell lines were treated with a pharmacological inhibitor for MEK, mirdametinib (10 nM), and selumetinib (20 nM) for 48 h and analyzed the expression of Furin, pMEK1/2, MEK1/2, pERK1/2, ERK1/2 by immunoblotting (n = 3). (D) Selumetinib downregulates MEK/ERK signaling cascade in furin‐expressing cells. TPC‐1 cells carrying FURIN cDNA were treated with selumetinib (20 nM) for 48 h. Cells were lysed and proteins were immuno‐blotted with antibodies against Furin, pMEK1/2, MEK1/2, pERK1/2, ERK1/2, and β‐Actin as indicated (n = 3). (E) The co‐inhibition of MEK and furin further downregulate MEK/ERK signaling cascade in PTC cells. PTC cells were transfected with FURIN shRNA, and treated with selumetinib (20 nM) for 48 h. Cells were lysed and proteins were immuno‐blotted with antibodies against Furin, pMEK1/2, MEK1/2, pERK1/2, ERK1/2, and β‐Actin as indicated (n = 3).
