Fig. 12.
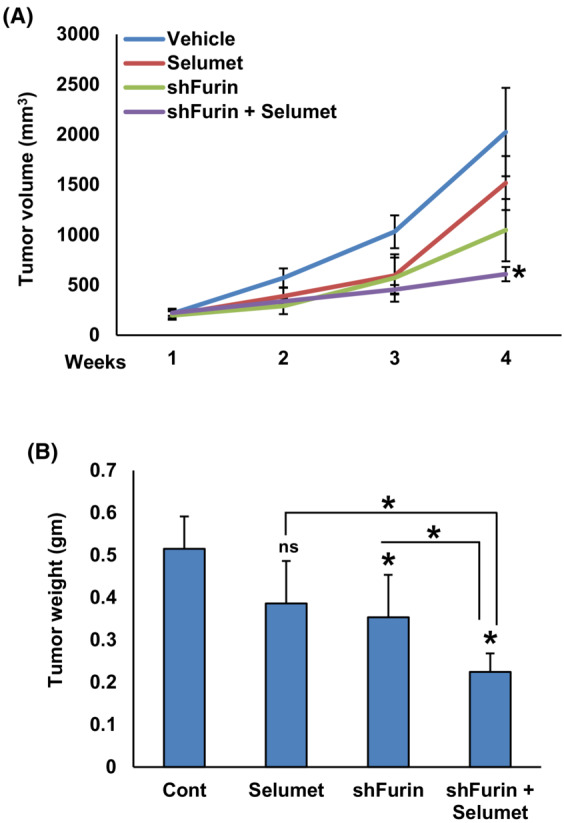
Depletion of furin potentiated the antitumor effect of selumetinib in vivo. NU/J mice were divided into four groups (n = 5) and the first two groups of mice were inoculated with BCPAP‐pRS cells (empty vector) and were treated with vehicle (0.1% DMSO, i.p) and selumetinib (10 mg·kg−1, i.p) respectively. The third and fourth groups of mice were inoculated with BCPAP‐pRS‐shfurin cells and treated with vehicle (0.1% DMSO, i.p) and selumetinib (10 mg·kg−1, i.p) respectively. After tumors grew to about 100 mm3, mice were treated intraperitoneally with selumetinib (10 mg·kg−1) and vehicle (0.1% DMSO), twice a week for 30 days. The tumor volume (A) and mouse body weight were monitored weekly. After 4 weeks, mice were sacrificed and individual tumors were weighed (B). Data were presented as mean ± SD (n = 5). Statistical analyses were performed using two‐tailed Student's t‐tests. *P < 0.05.
