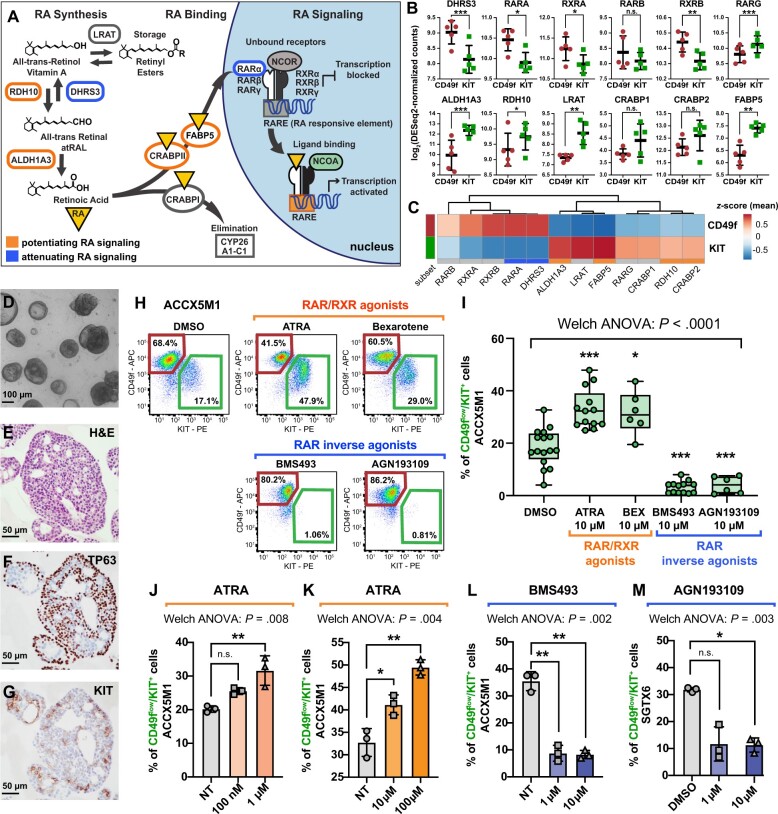
Figure 4.
The role of retinoic acid (RA) signaling in controlling the cell composition of human ACC organoids. A) Schematic modeling of the RA signaling pathway. B) Comparison of the gene-expression levels for known mediators of RA signaling in CD49fhigh/KITneg (CD49f) and CD49flow/KIT+ (KIT) cells, as measured by RNA-seq on autologous pairs from biphenotypic ACCs. Genes identified as attenuators of RA signaling displayed preferential expression in CD49fhigh/KITneg cells (CD49f), whereas genes identified as potentiators of RA signaling displayed preferential expression in CD49flow/KIT+ cells (KIT). Error bars: mean +/- standard deviation (n.s. = not significant; *P < .10; **P < .05; ***P < .01; Student’s t test, paired samples). C) Heatmap displaying mean-centered z scores for the average expression levels of modulators of RA signaling in CD49fhigh/KITneg (CD49f) and CD49flow/KIT+ (KIT) cells. D-G) Analysis by microscopy and IHC of 3D organoids established from human ACCs. Organoids consisted in large adenoid structures (D-E) that recapitulated key elements of the histological architecture of primary tumors, such as the coexistence of 2 cell types with mutually exclusive expression of TP63 (F) and KIT (G). H-I) Analysis by flow cytometry of ACCX5M1 organoids treated for 1 week with either agonists (ATRA, 10 µM; bexarotene, 10 µM) or inhibitors (BMS493, 10 µM; AGN193109, 10 µM) of RAR/RXR signaling. Treatment with agonists induced an increase in the percentage of CD49flow/KIT+ cells, whereas treatment with inhibitors resulted in their reduction. J-M) Dose-response studies of the effects of agonists and inhibitors of RAR/RXR signaling on the cell composition of human ACC organoids. Treatment with increasing concentrations of ATRA (0.1-100 µM) resulted in a progressive increase of the percentage of CD49flow/KIT+ cells (ACCX5M1 [J-K]). The effects of ATRA were already detectable at low concentrations (0.1-1 µM; ACCX5M1 [J]). Treatment with inhibitors of RAR/RXR signaling (BMS493, AGN193109) resulted in a profound reduction of the percentage of CD49flow/KIT+ cells, even at low pharmacological doses (1 µM; ACCX5M1 [L]; SGTX6 [M]). Changes in the percentage of CD49flow/KIT+ cells were evaluated by FACS and tested for statistical significance using Welch’s 1-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s T3 test (n.s. = not significant; *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001) assuming a normal distribution (Supplementary Figure 7, available online). 3D = 3-dimensional; ACC = adenoid cystic carcinoma; ANOVA = analysis of variance; APC = allophycocyanin; ATRA = all-trans retinoic acid; DMSO = dimethyl-sulfoxide; FACS = fluorescence-activated cell sorting; H&E = hematoxylin and eosin stain; IHC = immunohistochemistry; NT = untreated; PE = phycoerythrin; RA = retinoic acid; RAR = retinoic acid receptor; RNA-seq = RNA sequencing; RXR = retinoid X receptor.