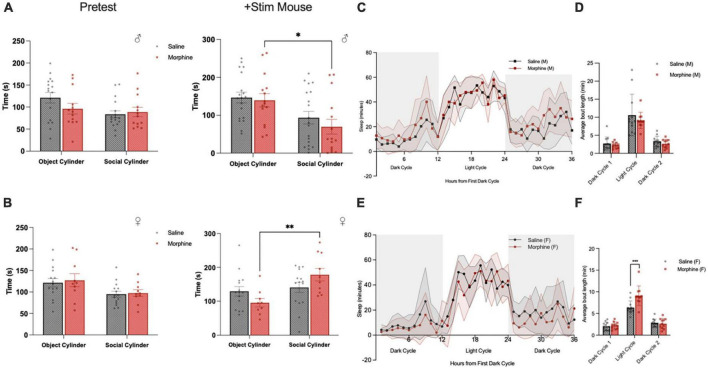
FIGURE 9.
3-Trimester NOWS alters social and sleep behavior in adulthood. (A) Time spent interacting with the object-paired and social-paired cylinder in 3-chamber social affiliation test in males during the pretest (empty cylinder phase) and with addition of a stimulus mouse. During the stimulus mouse phase, there was a significant effect of session [F(1, 18) = 13.3, *p < 0.05], but no session x NOWS treatment interaction [F(1, 10) = 0.23, p > 0.05]. Post hoc analysis revealed morphine males spent significantly less time interacting with the social cylinder than the object cylinder (p < 0.05), but there was no significant difference in saline males. (B) Time spent interacting with the object-paired and social-paired cylinder in 3-chamber social affiliation test in females during the pretest (empty cylinder phase) and with addition of a stimulus mouse. During the stimulus mouse phase, there was a significant effect of session [F(1, 45) = 8.8, **p < 0.01] and a significant session x NOWS treatment interaction [F(1, 45) = 5.1, p < 0.05]. Post hoc analysis revealed morphine females spent significantly more time interacting with the social cylinder than the object cylinder (p < 0.01), but there was no significant difference in saline males. (C) Time spent sleeping, as measured by the COMPASS system, in male mice. There was a significant effect of time [F(35,770) = 38.2, p < 0.001], and a significant time x NOWS treatment interaction [F(35,770) = 1.7, p < 0.01]. (D) Average sleep bout length in each light and dark period in male mice. There was a significant effect of time [F(2,44) = 1.6, p < 0.001], but no effect of NOWS treatment. (E) Time spent sleeping, as measured by the COMPASS system, in female mice. There was a significant effect of time [F(35,735) = 33.6, p < 0.001] and a modest time x NOWS treatment interaction [F(35,735) = 1.4, p < 0.1]. (F) Average sleep bout length in each light and dark period in female mice. There was a significant effect of time [F(2,52.6) = 139.9, p < 0.001], and a significant time x NOWS treatment interaction [F(2,52.6) = 9.3, p < 0.001]. Post hoc analysis revealed a significant difference in sleep bout length between NOWS and saline mice during the light period [χ2(1, N = 23) = 16.54, ***p < 0.001]. All data was generated from 11 total litters (6 saline, 7 NOWS).