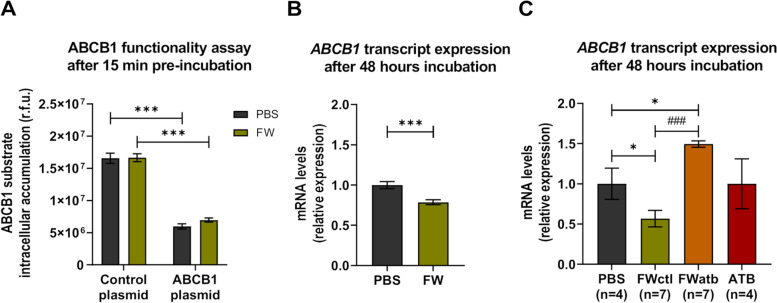
Fig. 8.
Polar bacterial metabolites impact the transcriptional regulation of ABCB1, but not directly its functionality. A ABCB1 substrate (rhodamine 123) intracellular accumulation (in relative fluorescent units, r.f.u.) with or without a 15 min pre-exposition to mouse faecal water (FW) in control plasmid or in ABCB1-transfected cells (n = 6/group, N = 2). ***p < 0.001. B Comparison of the mRNA expression of ABCB1 in control Caco-2 cells (PBS) or cells exposed to mouse FW for 48 h (n = 3/group, N = 5). ***p < 0.001. C Comparison of the mRNA expression of ABCB1 in control Caco-2 cells (PBS) or cells exposed for 48 h to FW from untreated mice (FWctl), or to FW from ATB-treated mice (FWatb), or to antibiotics (ATB) (n indicated on the figure, for FW n = 7 biological replicates). *p < 0.05 and.###p < 0.001 (paired t-test between FWctl and Fwatb)