FIGURE 1.
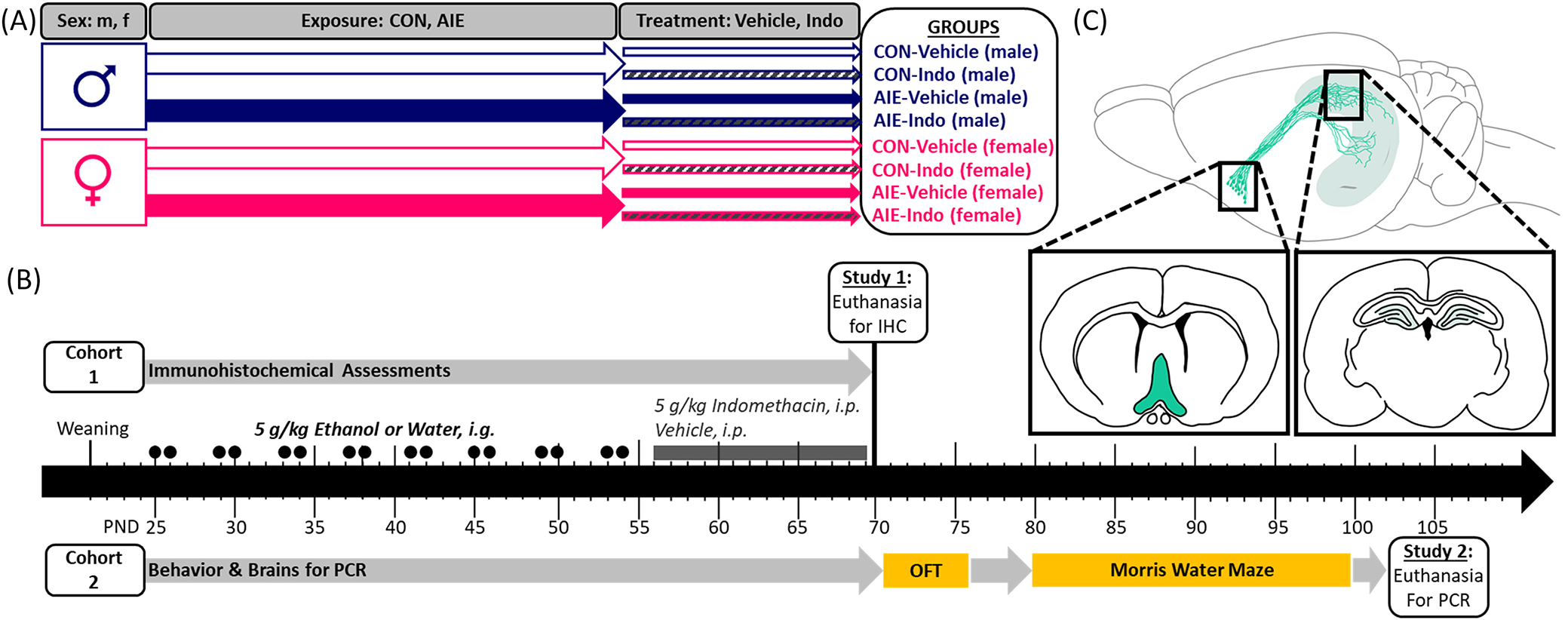
Experimental timeline. (A) The current experiments consisted of eight groups in a 2 × 2 × 2 design with the factors of sex (male, female), exposure (CON, AIE), and treatment (vehicle, Indomethacin). All animals were bred in-house and randomly assigned to treatment groups at weaning (PND 21) in a split-litter design. (B) Two separate cohorts of animals were run for two sets of experiments. The first cohort was utilized for IHC and the second underwent behavior, after which brains were processed for PCR. Starting on PND 25, exposure to either once daily intragastric intubation with water or 5 g/kg EtOH began. Rats were intubated in a 2-day-on/2-day-off cycle throughout adolescence. EtOH/water exposure stopped at PND 54. From PND 56–69, once daily intraperitoneal injections of 4 mg/kg indomethacin or vehicle (0.5% carboxymethylcellulose) began. Rats from Cohort 1 were euthanized on PND 70 for IHC. Cohort 2 continued after this time for behavioral analyses. Rats underwent the open field test to assess locomotion and thigmotaxis and afterwards performed the Morris water maze, which consisted of 6 days of acquisition training followed by 2 days of reversal training. All rats from experiment 2 were euthanized by PND 105 where the hippocampi were dissected for PCR. (C) Histological measures from Cohort 1 were performed on sections from the basal forebrain and dorsal hippocampus. PCR was performed on hippocampal dissections from Cohort 2.
