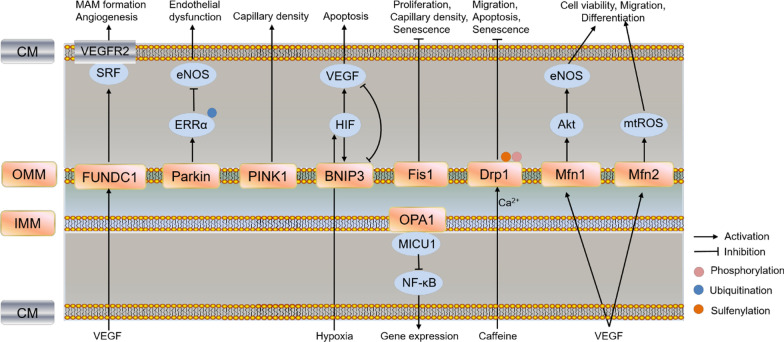
Fig. 4.
Schematic pathway of mitophagy and mitochondrial dynamics (including fusion and fission) in regulating ECs function and angiogenesis. Different colors of boxes indicate different locations of protein in cells listed on the left. PINK1 knockout impaired mitochondrial function, reduced cardiac capillary density and angiogenesis in heart; Parkin decreased eNOS expression and induced mitochondrial dysfunction by ubiquitination of ERRα; Deletion of FUNDC1 disrupted MAM formation and angiogenesis through decreasing binding of SRF to VEGFR2, and decreased VEGFR2 production; HIF-1-induced VEGF and BNIP3 regulated the balance between survival and apoptosis; Knockdown of Mfn2 led to mtROS production and mitochondrial dysfunction, and disrupted mitochondria-ER contact sites, while knockdown of Mfn1 reduced VEGF-induced Akt-eNOS signaling in HUVECs; Silencing Drp1 suppressed caffeine-induced lamellipodia formation and migration, while overexpression of Drp1 improved angiogenic function, and prevented apoptosis via mitochondrial Ca2+ dependent. Sulfenylation of Drp1 Cys644 and phosphorylation regulated ECs senescence; Fis1 increased proliferation, capillary density and angiogenesis, restored senescence phenotype in senescent EPCs. FUNDC1: FUN14 domain-containing 1; Parkin: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin; BNIP3: Bcl-2 nineteen-kilodalton interacting protein 3; Fis1: fission 1; Drp1: dynamin-related protein 1; Mfn1/2: mitofusins 1/2; OPA1: optic atrophy 1 protein 1; ERRα: estrogen-related receptor α; CM: cell membrane; OMM: outer mitochondrial membrane; IMM: inner mitochondrial membrane