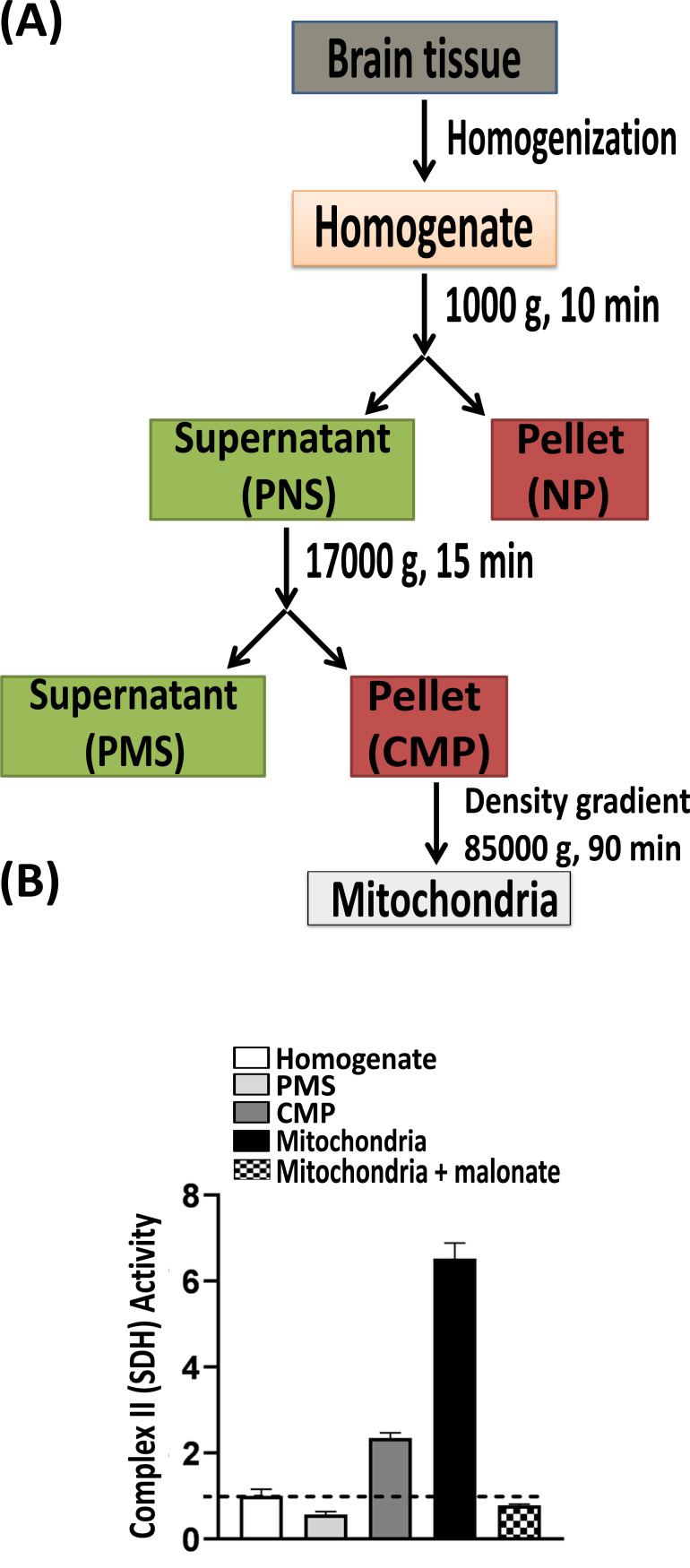
Fig. (1).
Biochemical isolation of brain mitochondria. (A) Flowchart reveals the basic protocol for isolation of mitochondria using an equilibrium density gradient sub-cellular fractionation protocol. The first slow speed centrifugation of the mechanically homogenized brain tissue sample results in a post nuclear supernatant (PNS) and a crude nuclear pellet (NP). Further high speed centrifugation of the PNS generates the crude mitochondrial pellet (CMP) and the cytosolic post mitochondrial supernatant (PMS). Pure free (nonsynaptic) mitochondria are separated from the CMP using density gradient centrifugation. (B) Assessment of enrichment (and integrity) of the mitochondrial fraction in comparison to the starting brain homogenate and other intermediate fractions can be performed using a spectrophotometric assay of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) activity (section 2.2.7.1; [61]). Malonate, a competitive SDH inhibitor was used to establish the specificity of the assay.