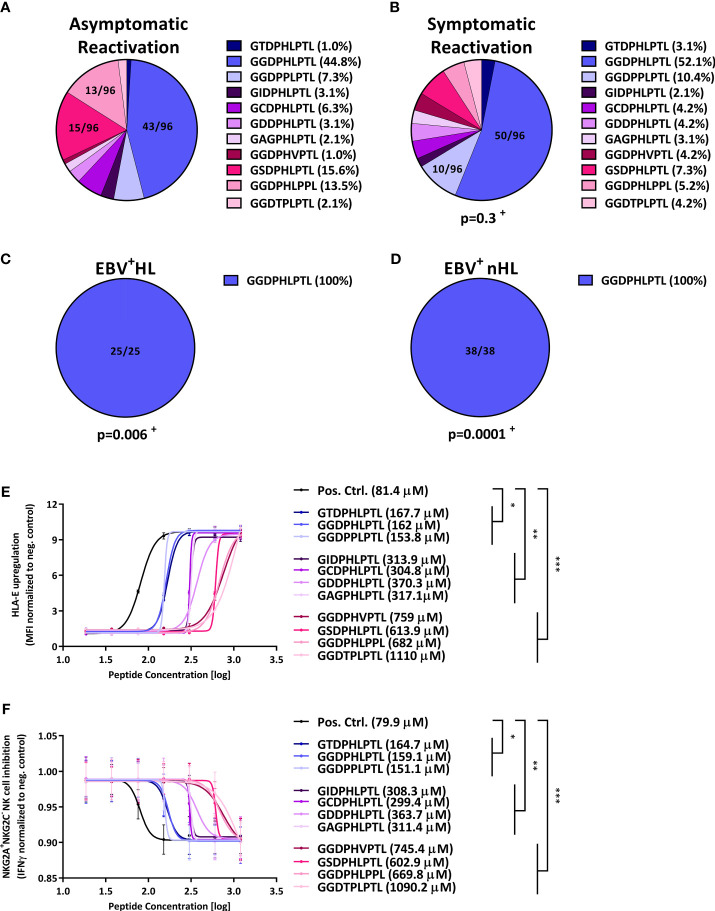
Figure 1.
LMP-1-derived peptides are associated with the development of EBV+ lymphomas and inhibit NKG2A+ NK cells. (A–D) Distribution of LMP-1 variants in patients with (A) asymptomatic reactivations (N=96), (B) symptomatic reactivations (N=96), (C) EBV+HL (N=25), (D) EBV+nHL (N=38). Fractions represent the relative frequency of the LMP-1 peptide GGDPHLPTL, GSDPHLPTL, GGDPHLPPL, GGDPPLPTL, GCDPHLPTL, GIDPHLPTL, GAGPHLPTL, GGDTPLPTL, GDDPHLPTL, GGDPHVPTL and GTDPHLPTL variants. + The frequency of the LMP-1 variants was compared to the asymptomatic cohort by the Chi2 Test. (E, F) HLA-E stabilisation assay. (E) HLA-E stabilisation assay: Raji cells were incubated with indicated concentrations of the positive control (VMAPRTLFL) or the LMP-1 peptide-derived GGDPHLPTL, GSDPHLPTL, GGDPHLPPL, GGDPPLPTL, GCDPHLPTL, GIDPHLPTL, GAGPHLPTL, GGDTPLPTL, GDDPHLPTL, GGDPHVPTL and GTDPHLPTL variants. The HLA-E surface expression was then assessed after 16h of co-culture by flow-cytometry. Plots represent the mean ( ± SD) of three independent replicates. Each peptide was compared to the positive control using RM one-way ANOVA (with the Geisser-Greenhouse correction). (F) NKG2A+NKG2C- NK cell inhibition assay: Raji cells were incubated with indicated concentrations of the positive control (VMAPRTLFL) or the LMP-1 peptide-derived GGDPHLPTL, GSDPHLPTL, GGDPHLPPL, GGDPPLPTL, GCDPHLPTL, GIDPHLPTL, GAGPHLPTL, GGDTPLPTL, GDDPHLPTL, GGDPHVPTL and GTDPHLPTL variants and were then co-cultured with pre-activated NKG2A+NKG2C- NK cells from 12 blood donors. Plots represent the mean ( ± SD) of 12 independent replicates. Each peptide was compared to the positive control using RM one-way ANOVA (with the Geisser-Greenhouse correction). p < 0.05 was considered significant. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. EBV+HL, EBV+ Hodgkin lymphoma, EBV+nHL, EBV+ non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Pos. Ctrl., positive control.