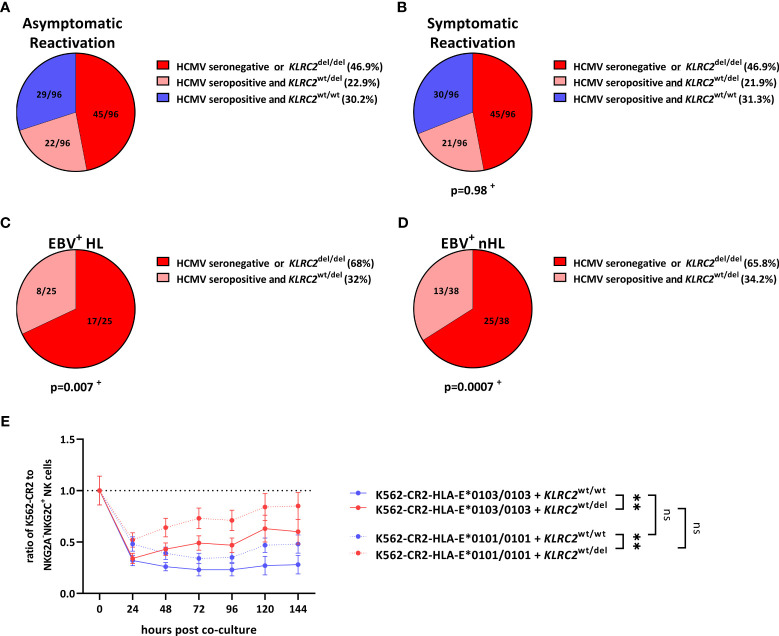
Figure 3.
KLRC2 variants are associated with the development of EBV+ lymphomas. (A–D) Distribution of KLRC2 variants in HCMV-seropositive and HCMV-seronegative individuals with (A) asymptomatic reactivations (N=96), (B) symptomatic reactivations (N=96), (C) EBV+HL (N=25), (D) EBV+nHL (N=38). Fractions represent the relative frequency of the KLRC2 variants in HCMV-seropositive and HCMV-seronegative individuals. + The frequency of the KLRC2 variants was compared to the asymptomatic cohort by the Chi2 Test. (E) Cell proliferation assays. Enriched NKG2A-NKG2C+ NK cells from 12 healthy blood donors encoding for the KLRC2 wt/wt (N=6) and KLRC2 wt/del (N=6) variant were co-cultured with EBV-infected K562-CR2-HLA-E*0103/0103 or K562-CR2-HLA-E*0101/0101 cells, pulsed with the LMP-1 GGDPHLPTL variant and were subsequently analysed by flow-cytometry. Plots represent the mean ( ± SD) of 6 independent replicates. RM one-way ANOVA (with the Geisser-Greenhouse correction) was used to compare the respective groups. p < 0.05 was considered significant. **p < 0.01. del, deletion, EBV+HL, EBV+ Hodgkin lymphomas, EBV+nHL, EBV+ non-Hodgkin lymphomas, ns, not significant, wt, wild type.