Figure 7.
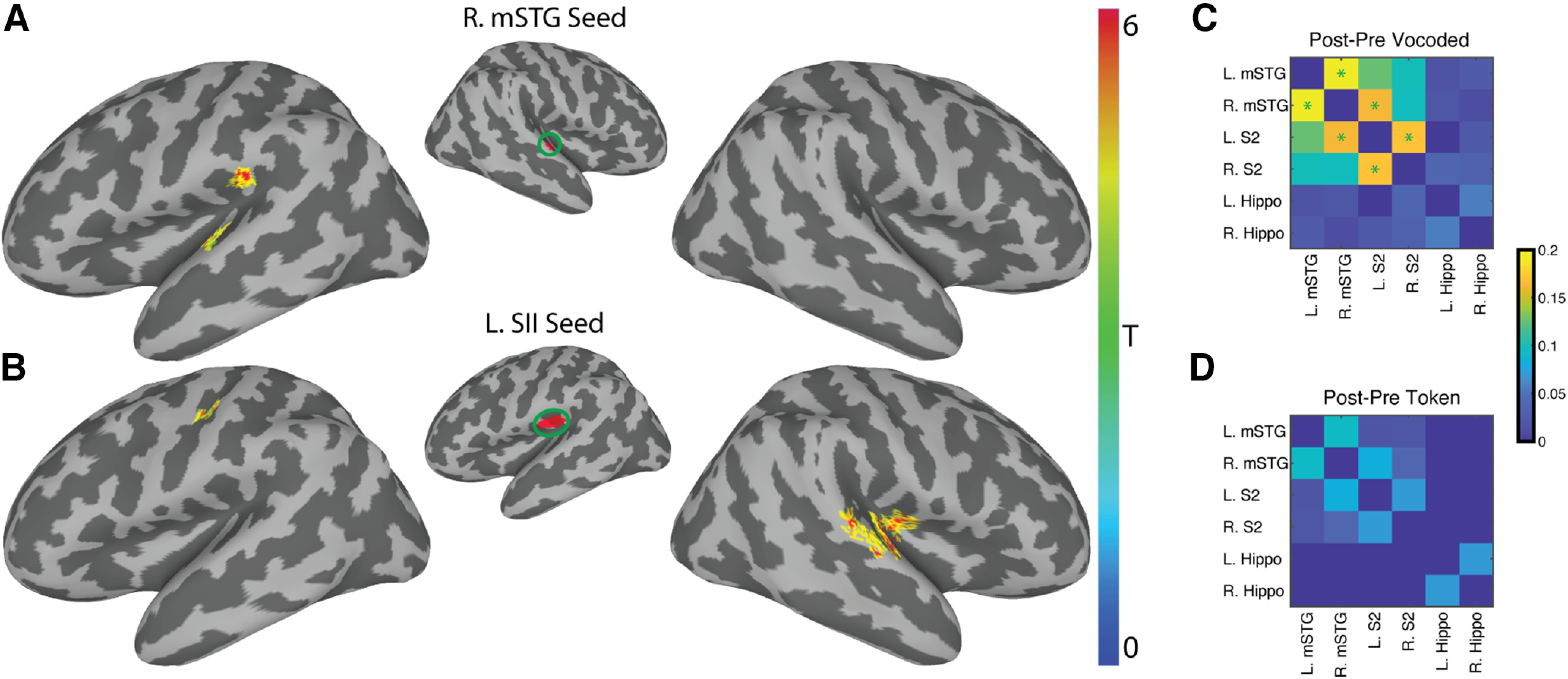
Training with vocoded VT speech stimuli increases functional connectivity between somatosensory and auditory regions. A, Using the right mid-STG ROI (Fig. 5) as a seed revealed two significant clusters of increased functional connectivity after training in the left STG (MNI: −50, −19, 7) and in the left supramarginal gyrus (MNI: −55, −28, 21). B, Using the left SII seed derived from the HCP-MMP1.0 atlas (Glasser et al., 2016) revealed a significant cluster in the left central sulcus (MNI: −40, −19, 42). It also identified two significant clusters in the right hemisphere. The first encompassed right insula and Heschl's gyrus (MNI: 40, −17, 11). The other is on the right STG (MNI: 63, −22, 7). All whole-brain results shown are corrected at two-tailed voxel-wise α = 0.005 and cluster p ≤ 0.05. Colors represent across-subject t statistics. C, D, The post-pre training correlations for the VT-vocoded and token-based groups, respectively, using an ROI-to-ROI functional connectivity. Color bar represents the post-pre training difference in functional connectivity between ROIs. A paired t test was performed to compare changes in functional connectivity post-pre training. Green asterisks represent p ≤ 0.05 FDR-corrected.
