Figure 6: Characterization of Vkg-GFP localization in Crag knocked down FCs.
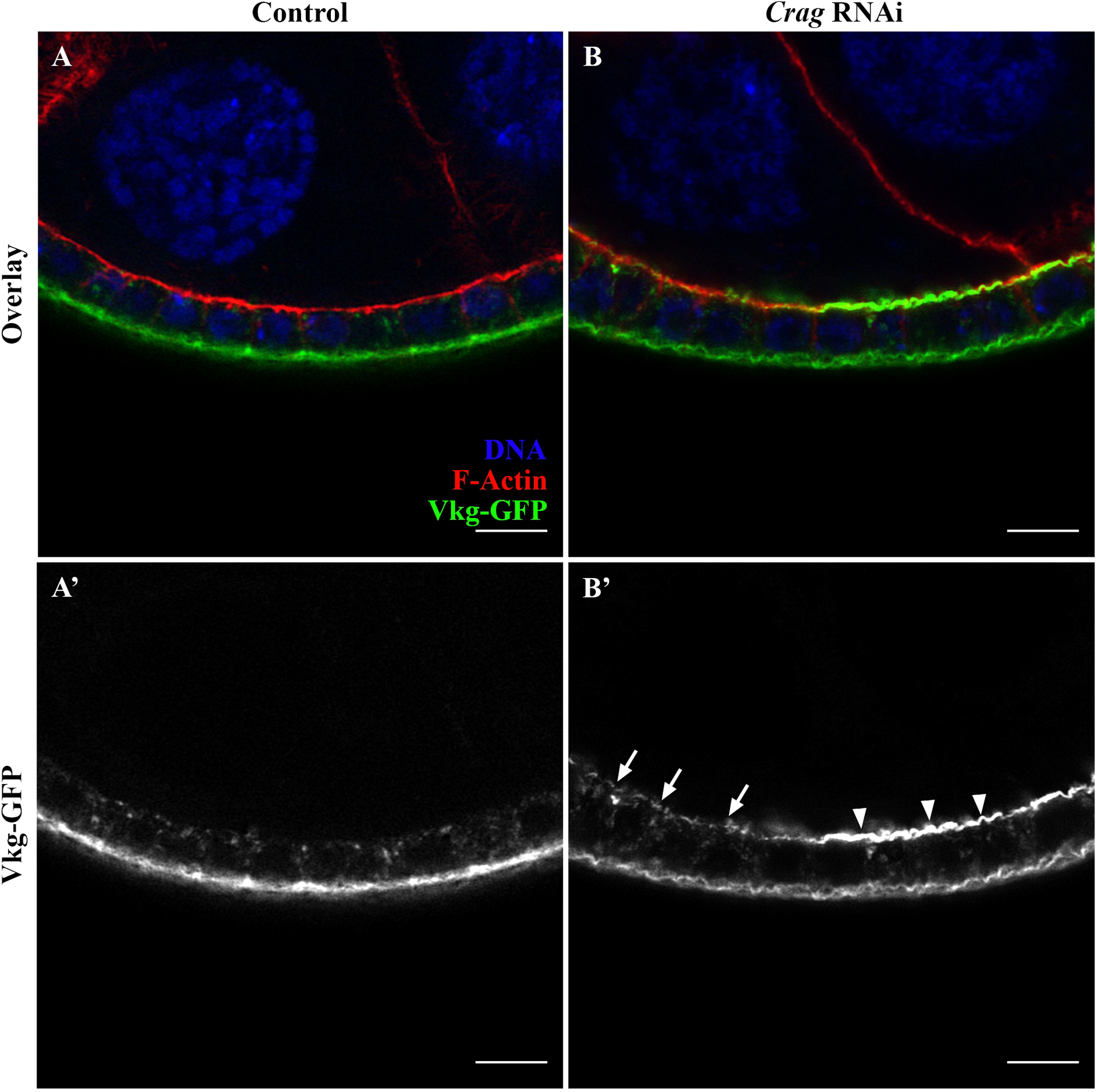
(A-B) Longitudinal section through an egg chamber expressing Vkg-GFP (green), stained for DNA (blue) and F-Actin (red) and acquired via optimal super-resolution processing. (A) Control line expressing wildtype Crag, a protein critical for proper BM deposition. The FE shows typical BM protein localization, wherein Vkg-GFP is intracellularly distributed and deposited basally in the FE (A’). (B) Transgenic Drosophila line expressing RNAi for Crag in the FE, resulting in a Crag knockdown. The loss of Crag leads to the mislocalization of BM proteins (e.g., Vkg-GFP) apically in the FE (B’, arrows and arrowheads). Super-resolution image is used to characterize the BM mislocalization phenotypes associated with the loss of Crag. Specifically, some Crag RNAi FCs, show a strong apical mislocalization of BM proteins (B’, arrowheads), while other Crag RNAi FCs present a weaker apical mislocalization (B’, arrows). Super-resolution imaging clearly reveals the phenotypes associated with the loss of Crag (B’, arrowheads vs arrows). Scale bars = 5 μm.
