Abstract
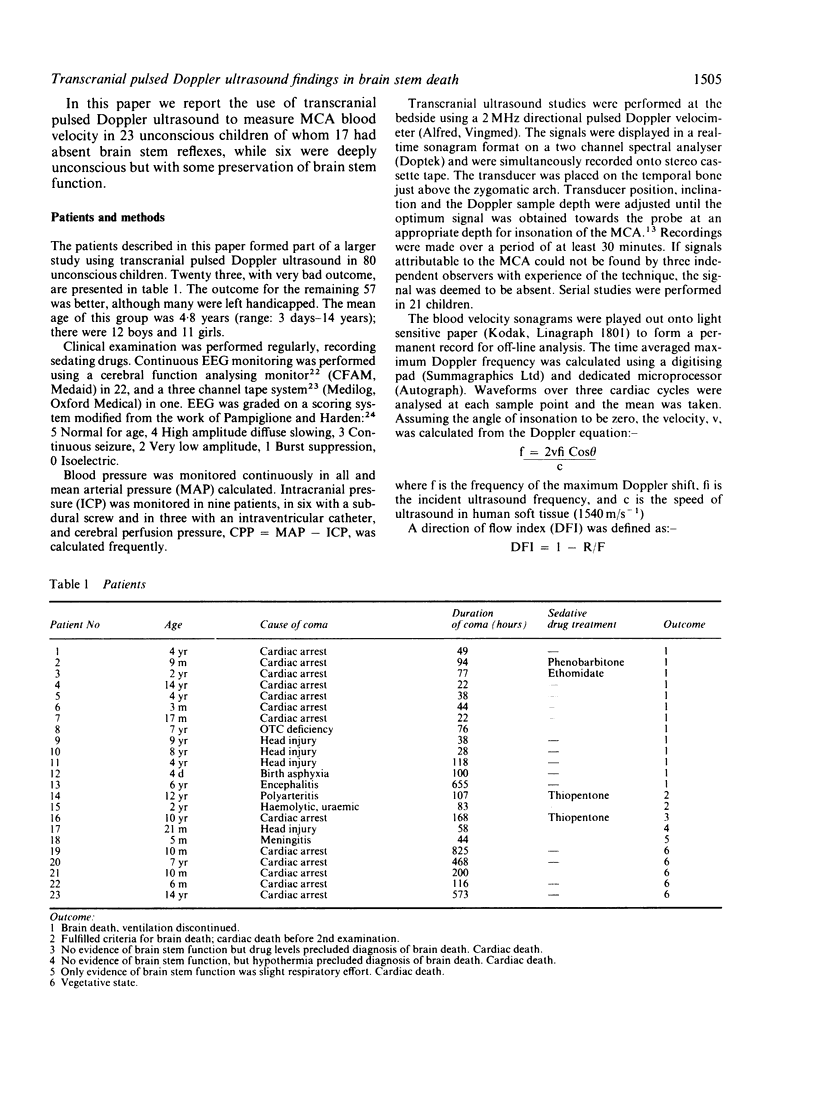
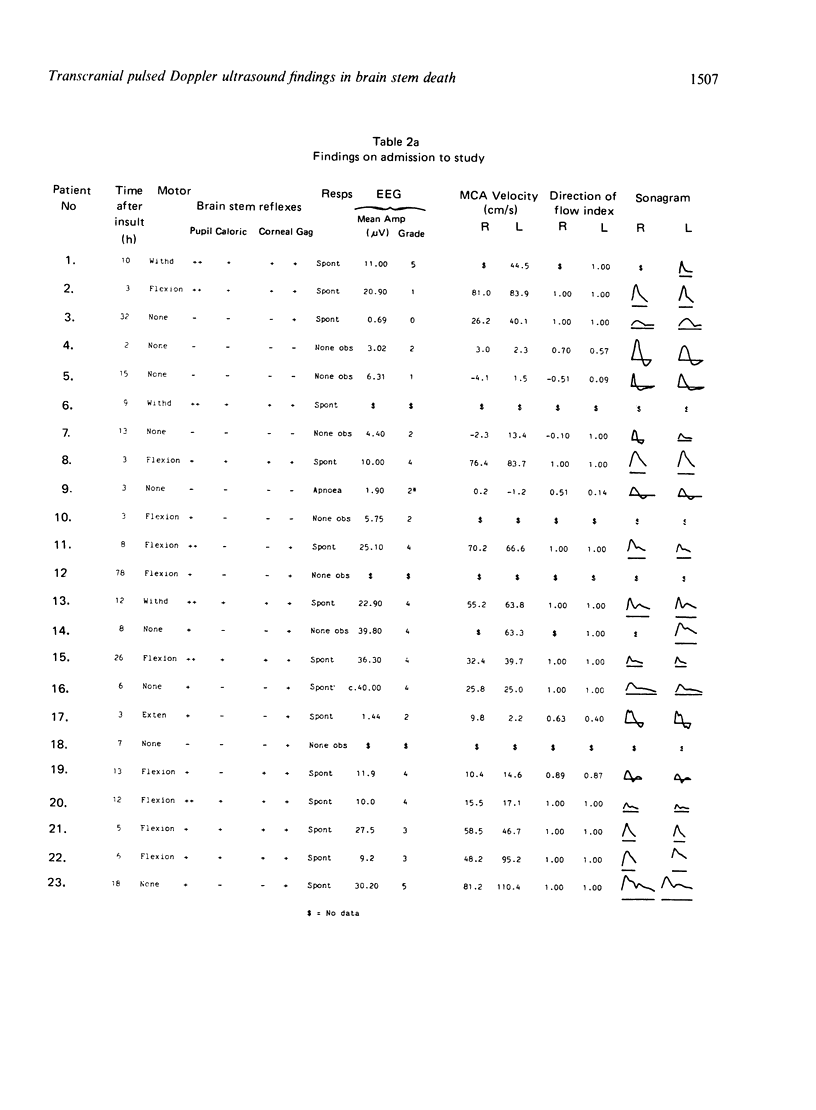
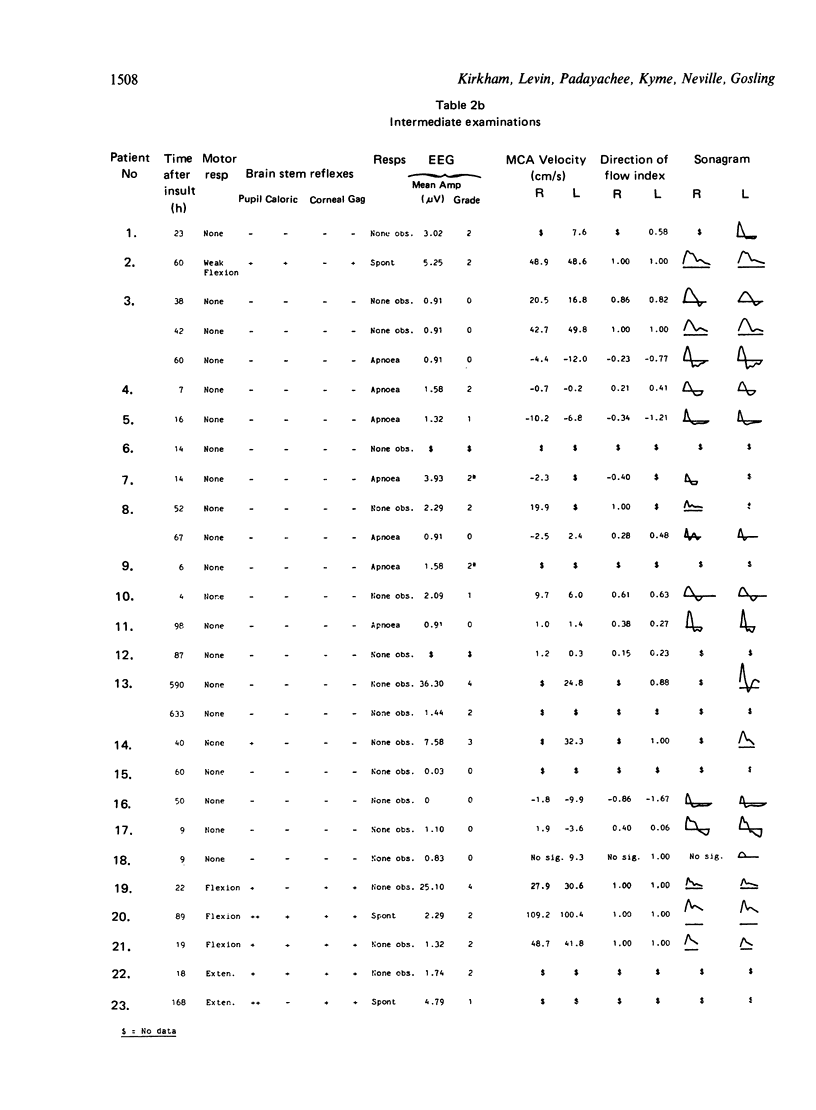
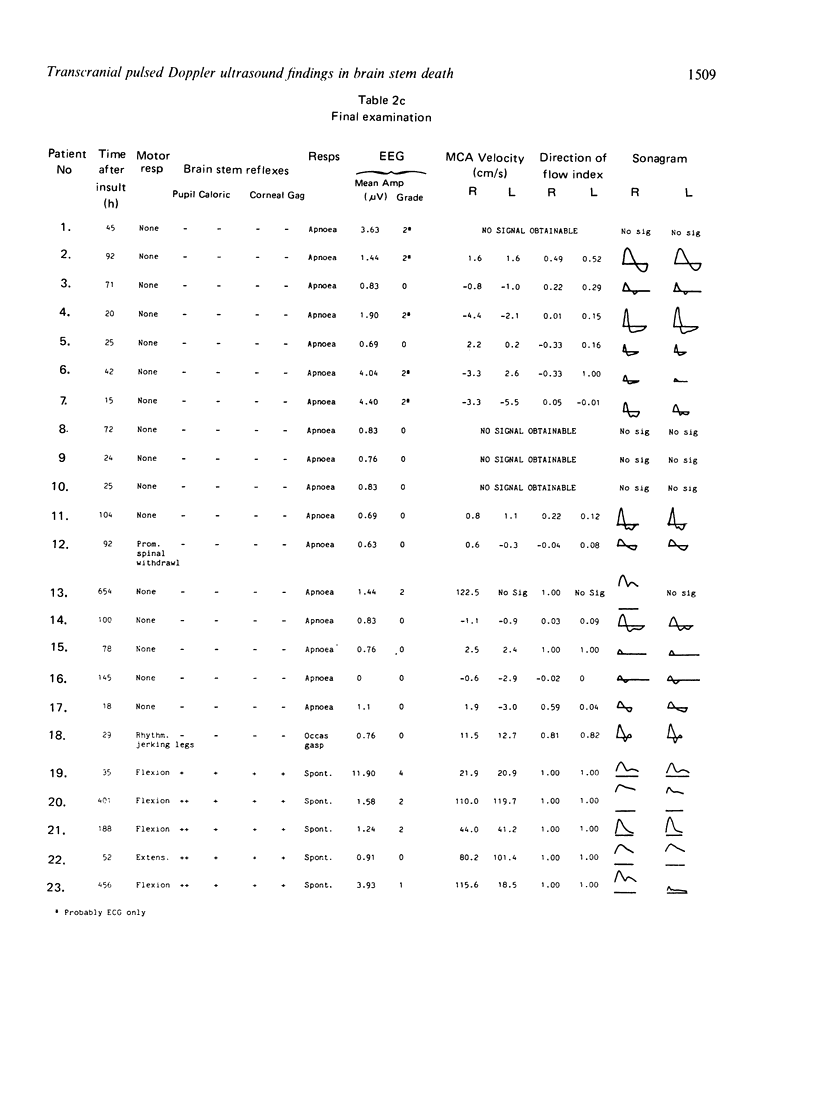
Data are presented from transcranial insonation of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) performed at intervals in 23 unconscious children for whom the outcome was subsequently poor. Once an MCA signal had been observed over a 30 minute period with time averaged velocity less than 10 cm s-1 and/or a direction of flow index, DFI, defined as 1 minus the ratio of reverse to forward flow of less than 0.8, recovery to forward flow throughout diastole was never observed and no patient recovered brain stem reflexes. Recovery of forward flow in diastole, and of brain stem function, was seen in cases with time averaged MCA velocity in the range 10 to 25 cm s-1 and with reverse flow but a DFI of greater than 0.8 for short periods of time. All but one of the 13 children fulfilling clinical criteria for brain stem death had MCA signals with time averaged velocity of less than 10 cm/s and DFI of less than 0.8. This type of signal was not observed in five children who were left in a persistent vegetative state.
Full text
PDF

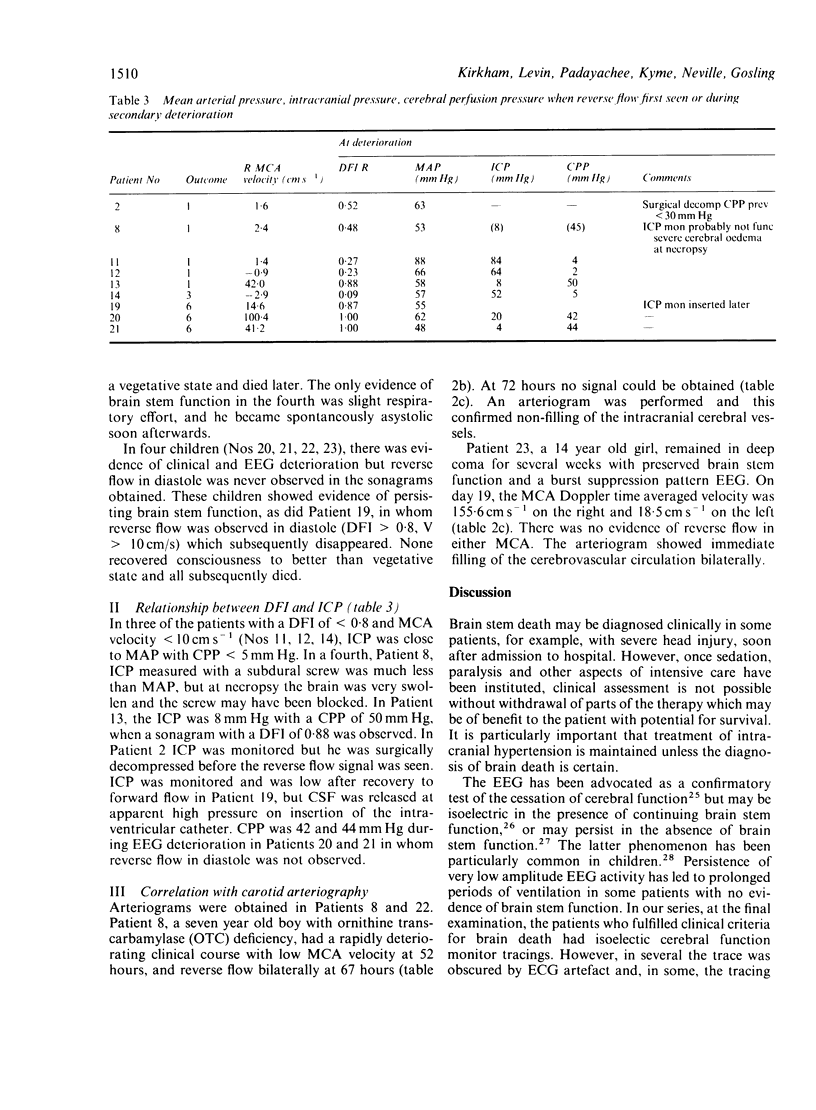



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaslid R., Markwalder T. M., Nornes H. Noninvasive transcranial Doppler ultrasound recording of flow velocity in basal cerebral arteries. J Neurosurg. 1982 Dec;57(6):769–774. doi: 10.3171/jns.1982.57.6.0769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen N., Burkholder J., Comiscioni J. Clinical criteria of brain death. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Nov 17;315:70–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb50331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwal S., Schneider S. Failure of electroencephalography to diagnose brain death in comatose children. Ann Neurol. 1979 Dec;6(6):512–517. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. R. The EEG in determination of brain death. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Nov 17;315:110–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb50334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bücheler E., Käufer C., Düx A. Zerebrale Angiographie zur Bestimmung des Hirntodes. Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Nuklearmed. 1970 Sep;113(3):278–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büdingen H. J., von Reutern G. M. Atraumatische Vorfelddiagnostik des Hirntodes mit der Doppler-Sonographie. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1979 Sep 21;104(38):1347–1351. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1129097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn A. W., Edmonds J. F., Barker G. A. Cerebral resuscitation in near-drowning. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1979 Aug;26(3):691–701. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)33757-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone R. K. Brain death. Am J Dis Child. 1983 Jun;137(6):545–546. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1983.02140320021002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Despland P. A., de Crousaz G. L'apport de l'ultrasonographie Doppler au diagnostic de la mort cérébrale. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1974 Oct 12;104(41):1454–1459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake B., Ashwal S., Schneider S. Determination of cerebral death in the pediatric intensive care unit. Pediatrics. 1986 Jul;78(1):107–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. H. Some aspects of the relationship between instantaneous volumetric blood flow and continuous wave Doppler ultrasound recordings--I. The effect of ultrasonic beam width on the output of maximum, mean and RMS frequency processors. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1982;8(6):605–609. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(82)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre J. A., Oozeer R. C., Wilkinson A. R. Diagnosis of neonatal seizure by continuous recording and rapid analysis of the electroencephalogram. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Oct;58(10):785–790. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.10.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard J. H., Kirkham F. J., Levin S. D., Neville B. G., Gosling R. G. Anatomical validation of middle cerebral artery position as identified by transcranial pulsed Doppler ultrasound. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Sep;49(9):1025–1029. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.9.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. M., Heck L. L. Confirmation of brain death at bedside by isotope angiography. JAMA. 1977 Aug 29;238(9):966–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greitz T., Gordon E., Kolmodin G., Widén L. Aortocranial and carotid angiography in determination of brain death. Neuroradiology. 1973 Feb;5(1):13–19. doi: 10.1007/BF02464624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzman B. H., Curless R. G., Sfakianakis G. N., Ajmone-Marsan C., Montes J. E. Radionuclide cerebral perfusion scintigraphy in determination of brain death in children. Neurology. 1983 Aug;33(8):1027–1031. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.8.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. B., Karle A., Rosenklint A. Changes in blood pressure and cardiac rhythm induced by arterial contrast injection. Neuroradiology. 1973 Aug;5(4):215–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00394738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkham F. J., Padayachee T. S., Parsons S., Seargeant L. S., House F. R., Gosling R. G. Transcranial measurement of blood velocities in the basal cerebral arteries using pulsed Doppler ultrasound: velocity as an index of flow. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1986 Jan;12(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(86)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korein J., Braunstein P., Kricheff I., Lieberman A., Chase N. Radioisotopic bolus technique as a test to detect circulatory deficit associated with cerebral death. 142 studies on 80 patients demonstrating the bedside use of an innocuous IV procedure as an adjunct in the diagnosis of cerebral death. Circulation. 1975 May;51(5):924–939. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.51.5.924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutzer E. W., Rutherford R. B., Lehman R. A. Diagnosis of brain death by common carotid artery velocity waveform analysis. Arch Neurol. 1982 Mar;39(3):136–139. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510150006002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langfitt T. W., Kassell N. F. Non-filling of cerebral vessels during angiography: correlation with intracranial pressure. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1966;14(1):96–104. doi: 10.1007/BF01401893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. R., Padayachee T. S., Beasley M. G., Keen H., Gosling R. G. Investigation of brian death with Doppler-shift ultrasound. J R Soc Med. 1983 Apr;76(4):308–310. doi: 10.1177/014107688307600415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard D. E., Jenkinson J. L. The cerebral function analysing monitor. Initial clinical experience, application and further development. Anaesthesia. 1984 Jul;39(7):678–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1984.tb06477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMenamin J. B., Volpe J. J. Doppler ultrasonography in the determination of neonatal brain death. Ann Neurol. 1983 Sep;14(3):302–307. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWilliam R. C., Stephenson J. B. Rapid bedside technique for intracranial pressure monitoring. Lancet. 1984 Jul 14;2(8394):73–75. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIBRAM H. F. Angiographic appearances in acute intracranial hypertension. Neurology. 1961 Jan;11:10–21. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.1.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padayachee T. S., Kirkham F. J., Lewis R. R., Gillard J., Hutchinson M. C., Gosling R. G. Transcranial measurement of blood velocities in the basal cerebral arteries using pulsed Doppler ultrasound: a method of assessing the Circle of Willis. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1986 Jan;12(1):5–14. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(86)90138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powner D. J. Drug-associated isoelectric EEGs. A hazard in brain-death certification. JAMA. 1976 Sep 6;236(10):1123–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIISHEDE J., ETHELBERG S. Angiographic changes in sudden and severe herniation of brain stem through tentorial incisure; report of five cases. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1953 Sep;70(3):399–409. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1953.02320330124011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenklint A., Jorgensen P. B. Evaluation of angiographic methods in the diagnosis of brain death. Correlation with local and systemic arterial pressure and intracranial pressure. Neuroradiology. 1974;7(4):215–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00342701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland T. W., Donnelly J. H., Jackson A. H., Jamroz S. B. Brain death in the pediatric intensive care unit. A clinical definition. Am J Dis Child. 1983 Jun;137(6):547–550. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1983.02140320023003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaywitz B. A., Rothstein P., Venes J. L. Monitoring and management of increased intracranial pressure in Reye syndrome: results in 29 children. Pediatrics. 1980 Aug;66(2):198–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Walker A. E. Cerebral blood flow and brain metabolism as indicators of cerebral death. A review. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1973 Aug;133(2):107–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudis E. V., Penry J. K., Link A. S., Jr Paradoxical contributions of EEG during protracted dying. Arch Neurol. 1984 Feb;41(2):153–156. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04050140051022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda S., Nishimoto A., Nukada T., Kuriyama Y., Katsurada K. To-and-fro movement and external escape of carotid arterial blood in brain death cases. A Doppler ultrasonic study. Stroke. 1974 Nov-Dec;5(6):707–713. doi: 10.1161/01.str.5.6.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



