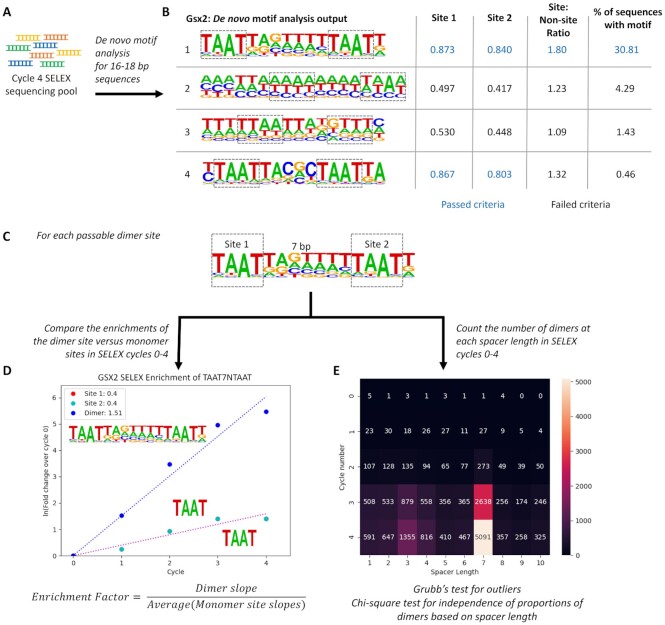
Figure 1.
The Cooperativity Predictor uses dimer to monomer site enrichment rates and spacer length constraints between sites to predict the cooperativity of HD TFs from HT-SELEX data. (A) A de novo motif analysis for long motifs (16–18bps) was performed using the cycle 4 sequencing pool of HT-SELEX for each HD TF. (B) The two 4mers with the highest information content within each PWM were selected to define each site. Each generated PWM was then interrogated for dimer sites using the following criteria: First, the information content of the two 4mer sites (Site 1 and Site 2) had to be greater than 0.6. Second, the information content of the 4mer sites must be 1.5 times greater than those of the surrounding regions. Third, the motif had to be present in at least 5% of the sequences in the cycle 4 sequencing pool. Note, those numbers shown in bold blue text passed the selected criterium. (C) For each dimer site that passed the selection criteria, the two 4mers and the spacer length were defined. (D) The percentage of sequences with dimer sites and monomer sites were determined after each cycle and used to calculate the fold changes of the dimer and monomer sites. Given the exponential nature of cycle amplification in PCR, the data was linearized through a natural log transformation. The enrichment factor is defined as the slope of the dimer enrichment over the average slopes of the 2 individual 4mer sites. (E) COSMO was used to count the number of dimers composed of the 2 4mers at each spacer length. Note, cycle 0 is the initial library prior to any selection process. The specific spacer length enrichment in cycle 4 was tested via a Grubb's test for outliers, and the dimer proportions between the initial library and cycle 4 were compared with a chi-square test for independence.