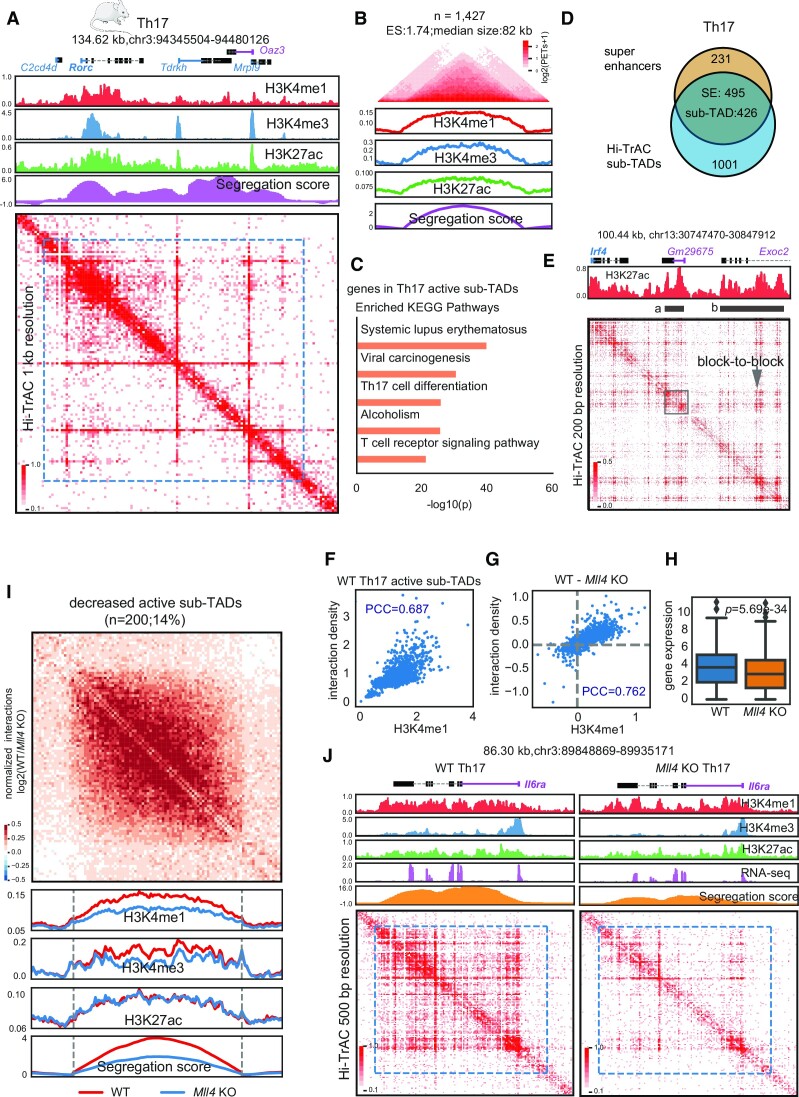
Figure 6.
Interactions within active sub-TADs are decreased by deletion of Mll4 in mouse Th17 cells. (A) The Rorc genomic locus, encoding a master transcription factor in Th17 cells, is located in an active sub-TADs. ChIP-seq and Hi-TrAC data were generated in this study (Supplemental Table 7). ChIP-seq signals were the average values from two replicates, and Hi-TrAC data were pooled from three biological replicates (Supplemental Table 7). (B) Aggregation analysis of 1427 active sub-TADs identified from Hi-TrAC data in mouse Th17 cells (Supplemental Table 9). (C) KEGG terms enrichment analysis for genes located within the Hi-TrAC active sub-TADs in mouse Th17 cells. Only the top 5 enriched terms were shown. (D) Overlaps of active sub-TADs and super-enhancers in mouse Th17 cells. (E) Example of active sub-TAD containing the Irf4 gene locus detected by Hi-TrAC showing block-to-block interaction pattern between super-enhancers. Two super-enhancers were marked as ‘a’ and ‘b’. Super-enhancer ‘a’ was highlighted with a gray box to show its internal structure. (F) Correlation analysis between H3K4me1 ChIP-seq signal intensities and Hi-TrAC interaction densities for wild-type Th17 cells active sub-TADs. PCC stands for Pearson Correlation Coefficient. (G) Correlation analysis between the changes in H3K4me1 ChIP-seq signal intensity and Hi-TrAC interaction density in active sub-TADs after deletion of Mll4 Th17 cells. (H) Distribution of expression levels for the genes located within the active sub-TADs. (I) Aggregation analysis of significantly decreased active sub-TADs based on segregation scores in Th17 cells comparing wild-type and Mll4 knockout mice (Supplemental Table 9). (J) Example of a significantly decreased active sub-TAD harboring the Il6ra gene important for Th17 function.