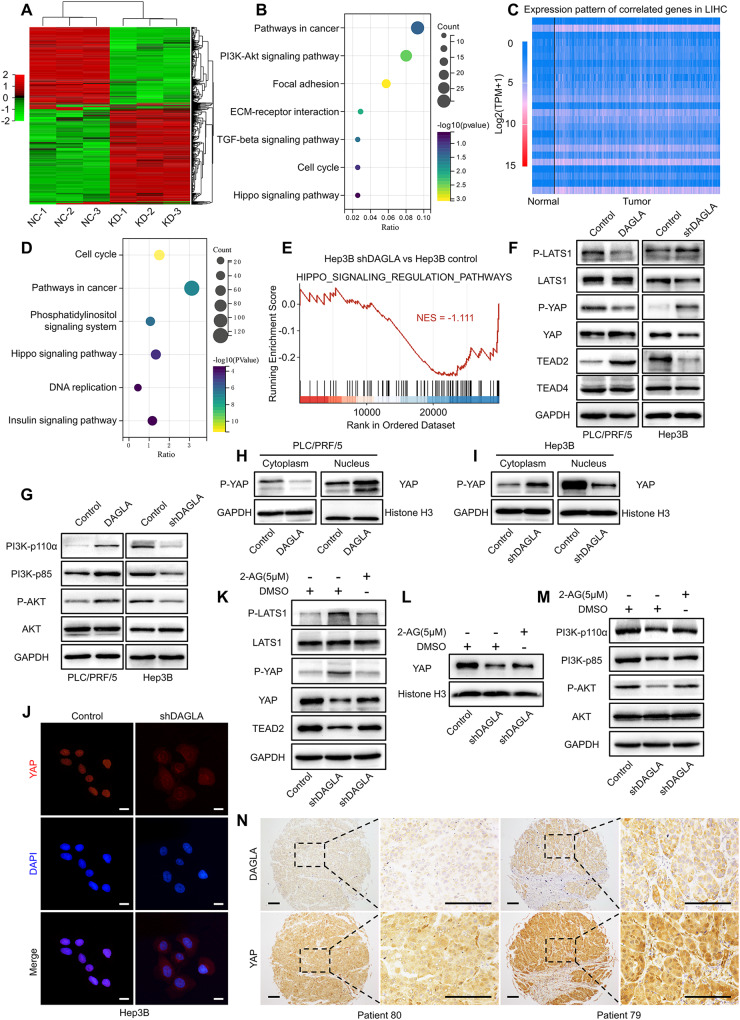
Fig. 3. The tumorigenic role of DAGLA in HCC is mediated by the Hippo and PI3K/AKT signalling pathways.
A Heatmap of the DEGs in Hep3B-shDAGLA cells compared with control cells. B KEGG analysis of downregulated DEGs in Hep3B-shDAGLA cells revealed the potential signalling pathways regulated by DAGLA in HCC. C Heatmap of the representative genes whose expression was correlated with DAGLA expression identified by TCGA database analysis with the filtering criteria of a correlation coefficient ≥0.3 and a P-value < 0.05. D KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of the gene set positively correlated with DAGLA showed the enriched signalling pathways correlated with DAGLA in HCC. E Gene set enrichment analysis of Hep3B-KD and control cells. The normalised enrichment score (NES) is shown. F, G Western blotting analysis confirmed the effects of DAGLA OE and KD on the Hippo and PI3K/AKT signalling pathways in HCC. H, I A nuclear/cytoplasmic protein extraction assay revealed that Hep3B-shDAGLA and PLC/PRF/5-DAGLA increased and decreased the phosphorylation level of YAP in the cytoplasm, respectively. J The IF assay indicated that DAGLA drove the nuclear translocation of YAP in HCC cells. Scale bars, 10 μm. K Hep3B-shDAGLA cells were treated with exogenous 2-AG (5 µM) for 48 h, and WB analysis was performed to detect changes in the expression of the indicated proteins. L WB showed that exogenous 2-AG rescued the low nuclear YAP level resulting from DAGLA knockdown. M WB was performed to detect the expression of the indicated proteins. N IHC staining of the HCC TMA revealed the correlation between high DAGLA expression and YAP nuclear translocation. Scale bars, 150 μm.