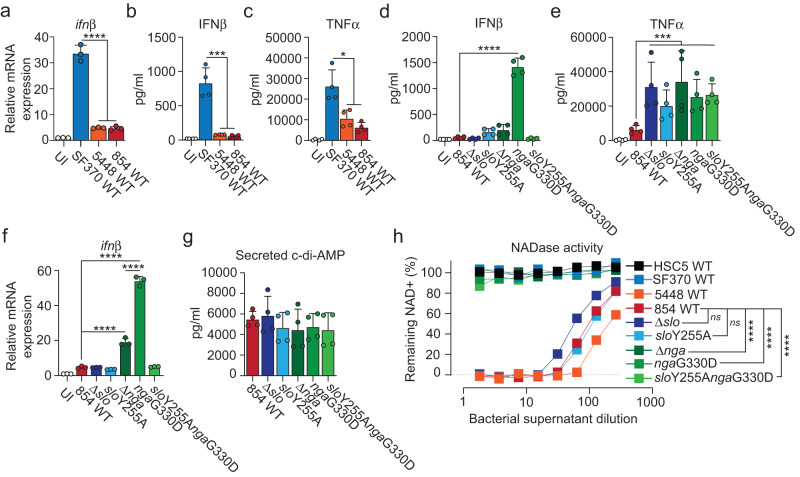
Fig. 2. Enzymatically active NADase inhibits type I IFN production in infected macrophages.
a Gene expression analysis of ifnβ in C57Bl/6 macrophages at 4 hpi with M1 strains SF370, 5448 or 854. Uninfected cells (UI) were analyzed as control. b, c ELISA-based analysis of secreted IFNβ (b) and TNFα (c) in similarly infected macrophages at 20 hpi. d, e Analysis of secreted IFNβ (d) and TNFα (e) from macrophages infected with 854 WT and thereof derived isogenic mutants, as indicated, at 20 hpi. f RTqPCR-based analysis of ifnβ expression at 4 hpi. g Secreted levels of c-di-AMP from 854 WT and isogenic mutants, as indicated. Results for gene expression analysis (mean and SD; n = 3), secreted c-di-AMP (mean and SD; n = 4) and cytokine secretion analyses (mean and SD; n = 4) representative of at least three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test. h Enzymatic activity of NADase in bacterial supernatants diluted as indicated was assessed by NAD degradation. Results based on at least three independent experiments. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test were used for multiple comparisons. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.