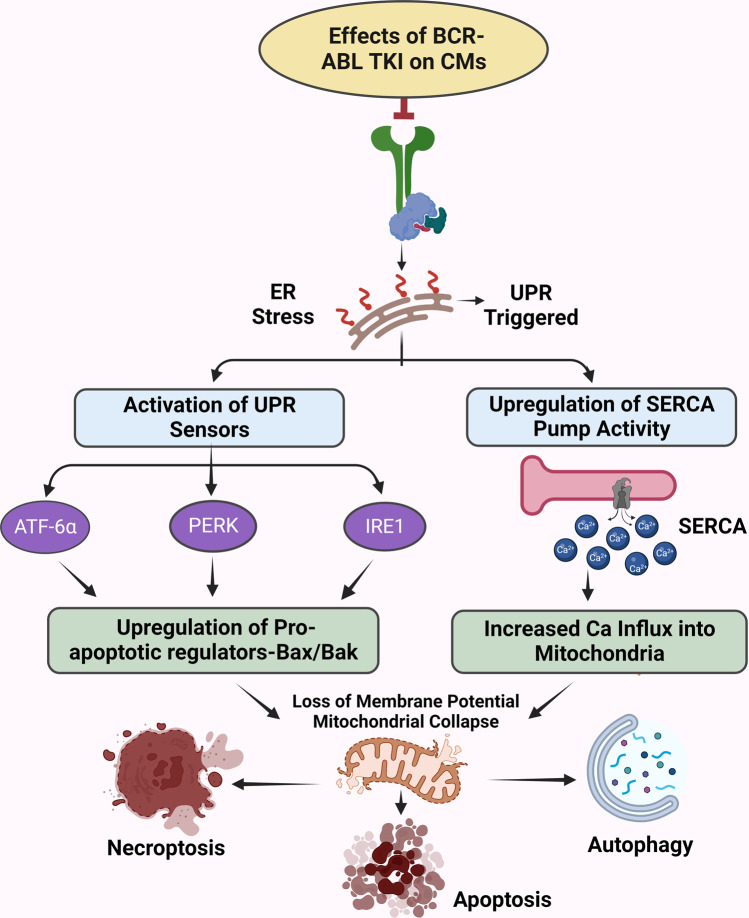
Fig. 1.
Proposed mechanisms of cardiovascular toxicity induced by on-target effects of BCR-ABL TKI. The on-target effect is defined as toxicity arising from the inhibition of the intended tyrosine kinase targets. Inhibition of BCR-ABL TK activity induces prolonged ER stress leading to stimulation of unfolded protein response (UPR) pathways. The UPR pathways constitute 3 major arms, including protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), inositol-requiring enzyme-1 α (IRE-1), and activating transcription factor 6 α (ATF6-α) transmembrane proteins of ER. When activated, PERK phosphorylates the eIF2α factor, which in turn leads to attenuation of protein synthesis. IRE-1-mediated downstream target activation of JNK signaling promotes both apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death. ATF6 is a basic leucine zipper transcription factor activated by translocation to the Golgi apparatus. ATF6 and ATF4 lead to the expression of CHOP, a pro-apoptotic transcription factor inducing cell death signaling. By activating pro-apoptotic proteins and inhibiting anti-apoptotic proteins, it directly activates Bax and Bak on the mitochondrial membrane. Altogether CHOP and JNK signaling produce significant mitochondrial dysfunction due to loss of MP, the release of cytochrome c, and ultimately apoptosis and necroptosis. Additionally, there is an abnormal sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca+2 ATPase pump (SERCA) activity in response to ER stress specifically due to calcium depletion in ER or activation of the UPR pathway. This results in increased calcium influx into mitochondria, the opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pore with a subsequent decline in ATP concentration, and markedly impaired energy generation. ATF4, Activating transcription factor 4; ATF6, Activating transcription factor 6; BAK, Bcl-2 antagonist/killer; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; BCL-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; BCR-ABL, breakpoint cluster region-Abelson; BCL-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Bid, BH3 interacting domain death agonist; Bim, Bcl-2-interacting mediator of cell death; Ca2+, Calcium; CHOP, C/EBP homologous protein; c-kit, Receptor tyrosine kinase; eIF2α, eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2α; ER, Endoplasmic Reticulum; IRE-1, Inositol-requiring transmembrane kinase/endoribonuclease; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MLKL, Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein; MP, Membrane Potential; PERK, protein kinase RNA like ER kinase; RIPK1, receptor-interacting serine/threonine kinase; SERCA, Sarcoendoplasmic Reticulum Calcium ATPase; SR, Sarcoplasmic Reticulum; TK, Tyrosine Kinase; TKI, Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor; UPR, unfolded protein response. The figures were created using scientific image and illustration software, BioRender (BioRender.com)