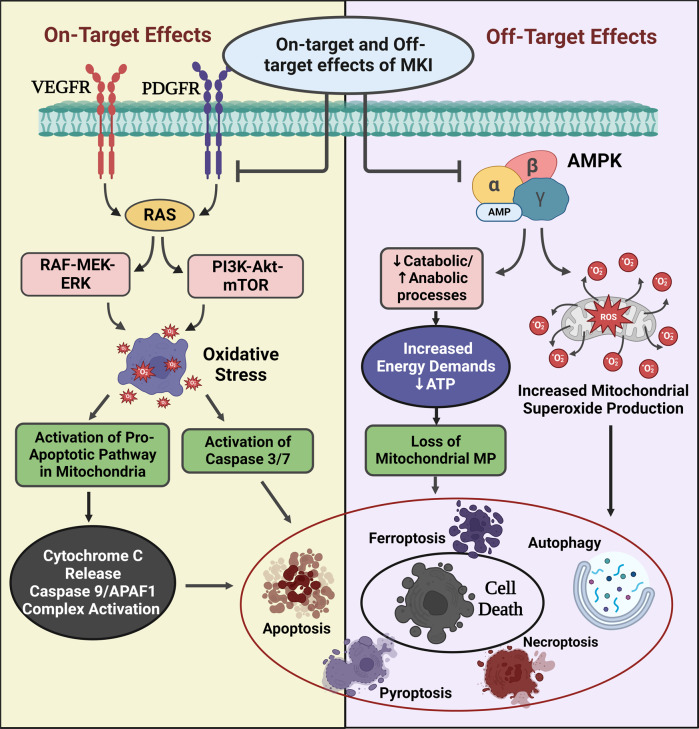
Fig. 2.
Proposed cellular mechanisms of on- and off-target effects of multi-kinase inhibitors. Off-target toxic effects are a result of the inhibition of kinases other than the intended target of the TKIs. Off-target blockage of AMPK by drugs like sunitinib leads to superoxide production in mitochondria resulting in cell death. Additionally, it inhibits catabolic processes such as glycolysis, GLUT 4 expression, and upregulation of anabolic processes such as glycogen synthesis, FA oxidation, and lipolysis which in turn leads to dysregulation of energy homeostasis in CMs along with ATP depletion and loss of membrane potential. It is also known to directly inhibit eIF2, resulting in the impairment of protein synthesis. Its on-target toxicity is mediated through the inhibition of PDGFR and VEGFR, which affects Raf-MEK-ERK and PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathways. This leads to oxidative stress and activation of pro-apoptotic pathways involving the release of Cyt c and activation of caspases and APAF1. Altogether these processes result in increased apoptosis, decreased cell survival and impaired compensatory myocardial response to stress, and ultimately cardiac contractile dysfunction. ATP, Adenosine tri-phosphate; Akt, Ak strain transforming; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; APAF 1, Apoptotic protease activating factor 1; ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; CaMKII, Calcium/Calmodulin Dependent Protein Kinase 2; CM, cardiomyocytes; Cyt C, Cytochrome C; ERK, Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; eIF2, FA, Fatty Acid; GLUT, Glucose transporter; MEK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MP, membrane potential; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; P, phosphate; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase; Raf, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; Ras, Rat sarcoma virus; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitors; VEGFR, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor. The figures were created using scientific image and illustration software, BioRender (BioRender.com)