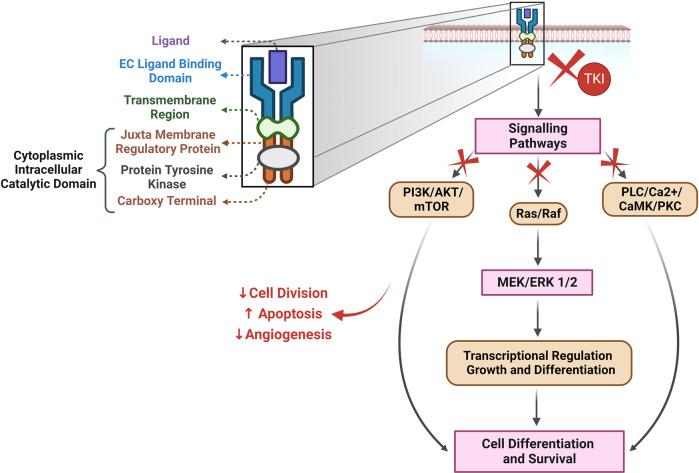
Fig. 5.
Receptor tyrosine kinase and its downstream pathways affected by tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Upon binding with the ligand the tyrosine kinase receptor gets activated resulting in the activation of multiple pathways, which are critical in cell survival, growth, and differentiation. Aberrant activation of these tyrosine kinase pathways is implicated in carcinogenesis. These effects are blunted by tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), which not only affect tumor growth but also hinder the function of normal cells in various organs, including cardiomyocytes in the heart. EC, extracellular; Akt, Ak strain transforming /protein kinase B; RAF, rapidly accelerate fibrosarcoma; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; Ca2+, Calcium; CAMK, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase; CM, cardiomyocyte; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; MEK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; PKC, Protein kinase C. The figures were created using scientific image and illustration software, BioRender (BioRender.com)