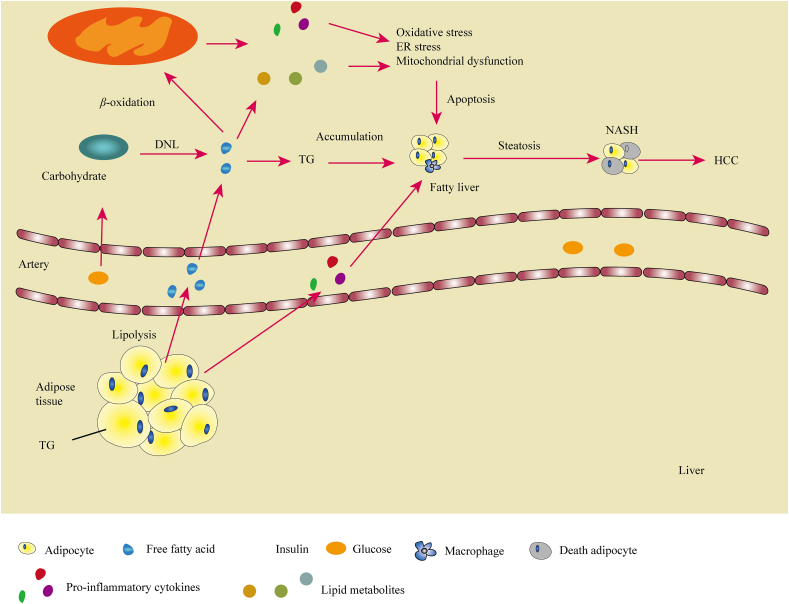
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the links between obesity and liver diseases. Free fatty acids (FFAs) and glucose from the circulation accumulate in the liver and support de novo lipogenesis (DNL) of FAs to form triglycerides (TG), which causes fatty liver. Under the ‘second hit’ of inflammation induced by oxidative stress, ER stress and reactive oxygen species (ROS) cause adipocyte apoptosis, which eventually leads to NASH and sometimes to HCC.