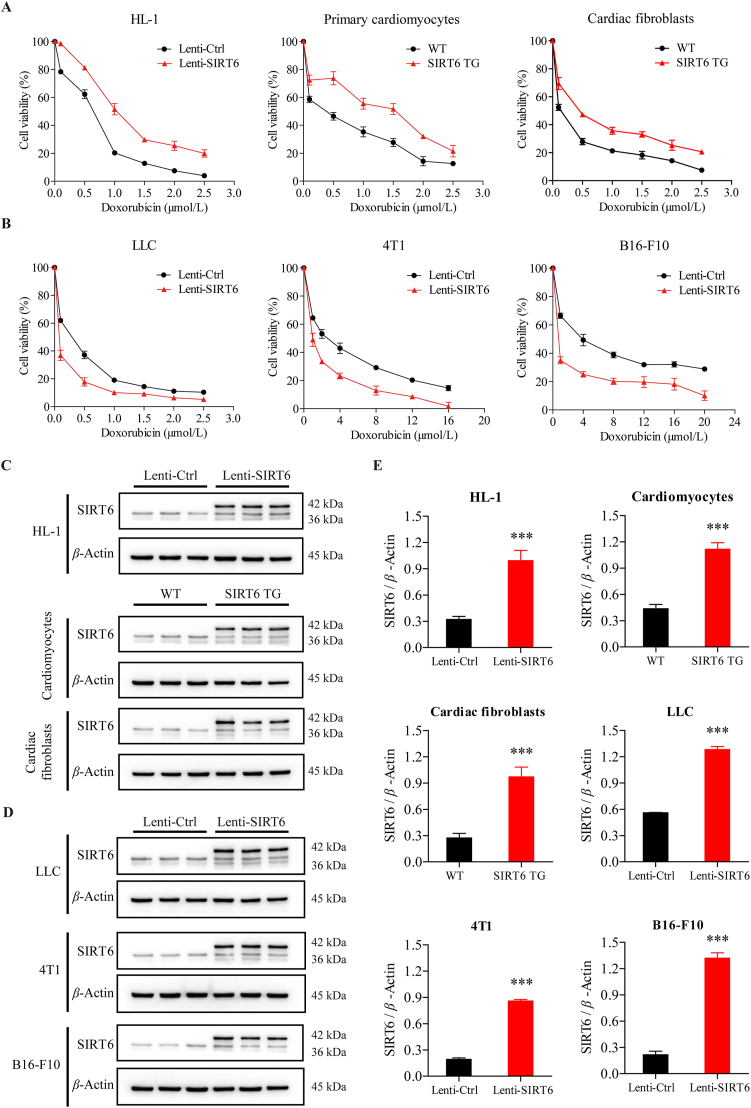
Figure 2.
Ectopic SIRT6 overexpression ameliorates Dox-induced cytotoxicity in cardiomyocytes but exacerbates Dox-induced cytotoxicity in cancer cells. (A, B) After treatment with different concentrations of doxorubicin (Dox) for 24 h, the viability of primary cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts isolated from SIRT6 transgenic (TG) mice and wild-type (WT) littermates, mouse cardiomyocyte HL-1 cells, mouse Lewis lung carcinoma LLC cells, mouse breast cancer 4T1 cells, and mouse melanoma B16-F10 cells infected with lentivirus containing SIRT6 vector (Lenti-SIRT6) or control vector (Lenti-Ctrl) was assessed by the CCK-8 method (n = 3 different experiments). (C, D) The protein expression of SIRT6 in HL-1 cells, primary cardiomyocytes, cardiac fibroblasts, LLC cells, 4T1 cells, and B16-F10 cells was detected by Western blotting. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (E) Semiquantitative analyses of bands were performed using ImageJ software (n = 3 different experiments). The data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Two-tailed unpaired t tests were performed to determine significant differences. ∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared to the control group.