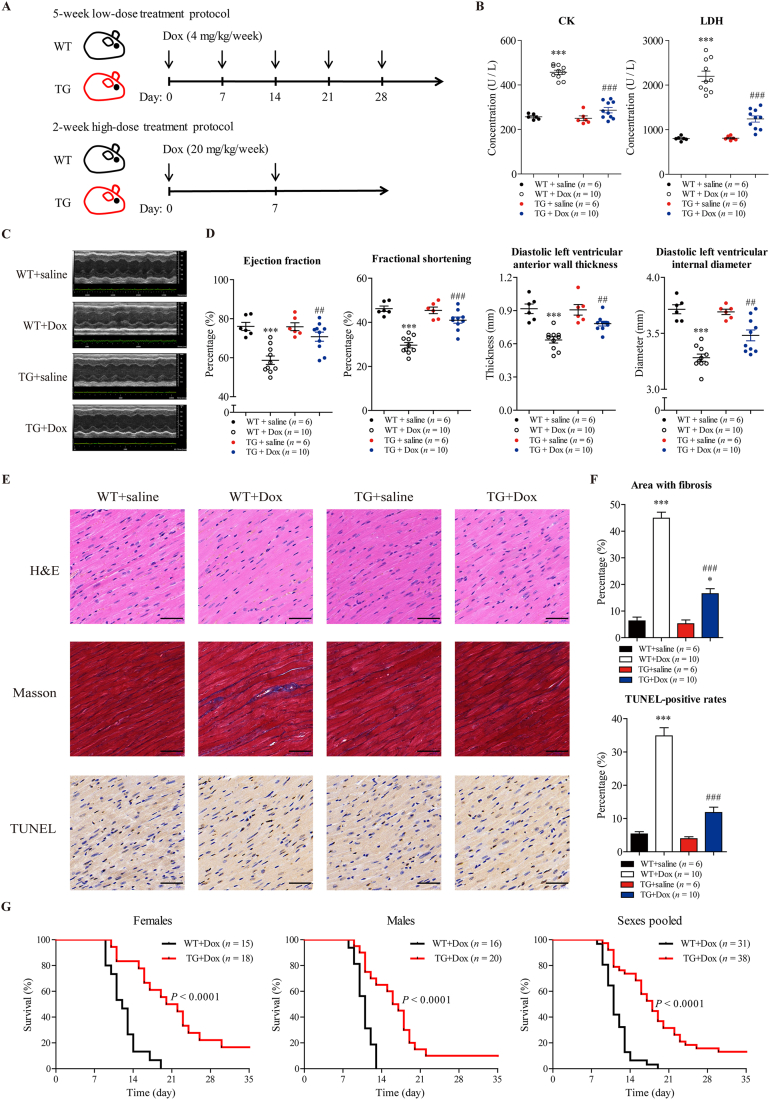
Figure 3.
SIRT6 overexpression ameliorates Dox-induced cardiotoxicity in mice. (A) The chronic low-dose treatment protocol and acute high-dose treatment protocol are shown. In the chronic treatment protocol, SIRT6 transgenic mice and wild-type littermates were injected with Dox (4 mg/kg/week, i.v.) or saline for 5 weeks, and the total cumulative dose was 20 mg/kg. In the acute treatment protocol, wild-type and SIRT6 transgenic mice were injected with Dox (20 mg/kg/week, i.v.) or saline for 2 weeks. (B) In the chronic treatment protocol, biochemical parameters associated with heart failure were measured in the plasma of the mice. The levels of CK-MB and LDH1 are shown in Fig. S1 (n = 6 or 10 animals per group). (C, D) In the chronic treatment protocol, cardiac function was measured using echocardiography and was assessed by ejection fraction, fractional shortening, diastolic left ventricular anterior wall thickness, and diastolic left ventricular internal diameter (n = 6 or 10 animals per group). (E) In the chronic treatment protocol, fibrosis, apoptosis and cell morphology in cardiac tissue were measured by Masson trichrome staining, TUNEL and H&E staining, respectively. Representative images were shown. Scale bar = 50 μm. (F) Quantitative analyses of the fibrotic area (blue-stained) and TUNEL-positive cells (brown-stained) in E were performed by ImageJ software (n = 6 or 10 animals per group). The data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of mean. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni multiple comparisons were performed to determine significant differences. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared to saline-treated WT mice. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ###P < 0.001 compared to Dox-treated WT mice. (G) In the acute treatment protocol, survival of wild-type and SIRT6 transgenic mice was observed daily (n = 15 to 20 animals per group). P values were calculated by the log-rank test.