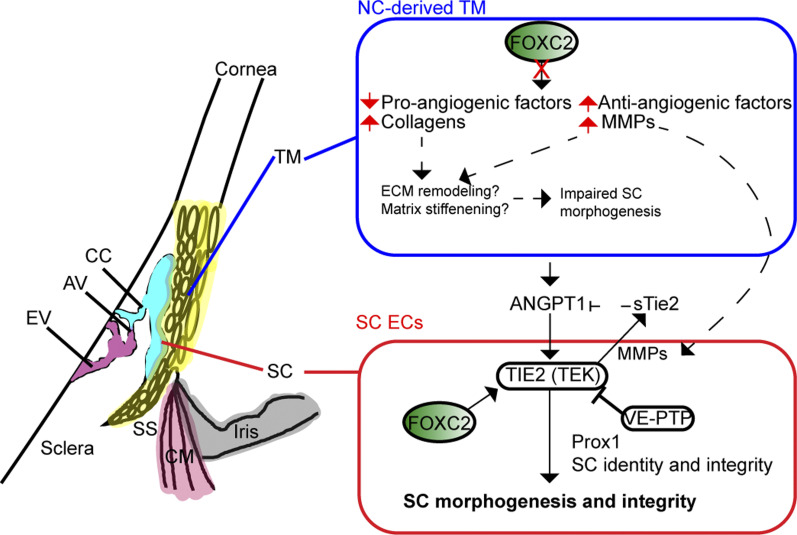
Figure 9. Neural crest- and endothelial- derived Foxc2 differentially regulate proper morphogenesis of the SC.
Neural crest-specific deletion of Foxc2 results in several transcriptional changes in the trabecular meshwork including the decrease in expression of pro-angiogenic factors and in contrast an increase in the expression of anti-angiogenic factors, collagens, and MMPs that likely result in abnormal ECM remodeling, matrix stiffening, and induction of TIE2 shedding that potentially contribute to impaired SC morphogenesis. In contrast, endothelial-derived Foxc2 regulates the expression of TIE2 to promote ANGPT1-mediated activation of the TIE2 receptor and, in turn, proper SC morphogenesis and maintenance of SC integrity. TM, trabecular meshwork; SC, Schlemm’s canal; SS, scleral spur; CM, ciliary muscle; CC, collector channel; AV, aqueous veins; EV, episcleral veins.