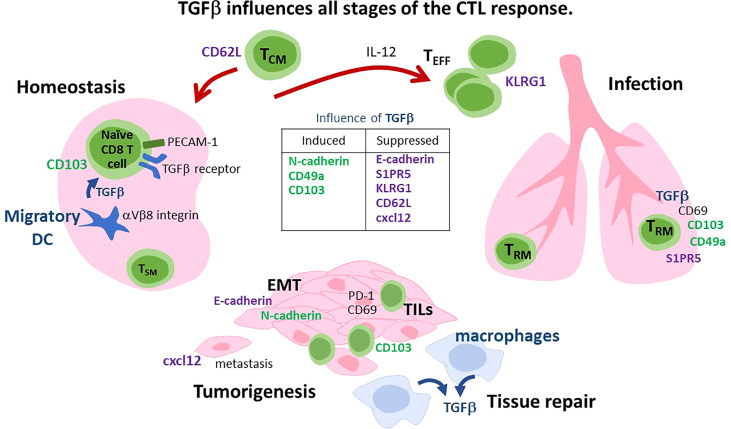
Figure 1.
Diverse functions for TGFβ during the CTL response. i) Homeostasis: PECAM-1 is expressed on naïve CD8 T cells and interacts with the TGFβ receptor to inhibit autoimmunity. Some naïve CD8 T cells are preconditioned to become TRM cells by migratory DC that express αVβ8 integrin and activate TGFβ. CD62L is lymphoid homing receptor that can be downregulated by TGFβ. ii) Infection. IL-12 overrides the suppress effects of TGFβ to enhance TEFF and TCM formation. TRM cells express adhesion molecules (CD103 and CD49a) that are induced by TGFβ, while S1PR5 is downregulated. Signaling via CD69 increases TGFβ production in the spleen. iii) Tumorigenesis and tissue repair. TGFβ is an angiogenic factor that promotes tumor growth and tissue repair. During EMT, TGFβ induces a ‘cadherin-switch’ by downregulating E-cadherin and inducing N-cadherin expression on mural cells. Macrophages are an important source of TGFβ during tissue repair. Specialized subsets of CTLs express cadherin-binding proteins (KLRG1 and CD103) and reside at barrier surfaces. CD103+ TRM cells mobilize from draining lymph nodes to the tumor when TGFβ signaling is disrupted. CTLs are excluded from tumors when CXC12 is expressed. Cancer cells undergo EMT in the presence of TGFβ. CXCL12 can be downregulated by TGFβ.