Figure 1.
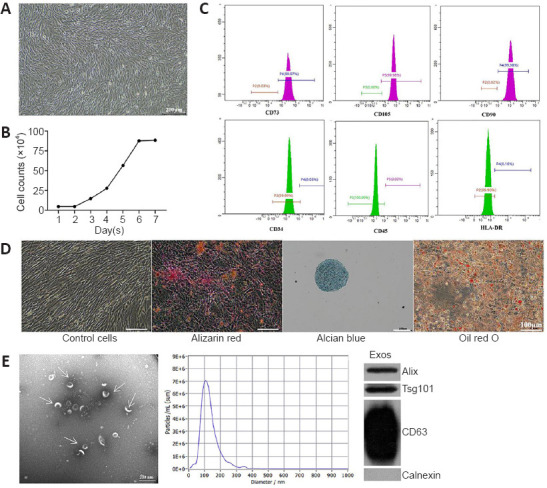
Typical characteristics of hucMSCs and hucMSC-Exos.
(A) Morphology of hucMSCs. Scale bar: 200 μm. (B) hucMSCs growth curve. The cells displayed a logarithmic growth followed by a static growth period, which is in line with the growth of stem cell populations. (C) hucMSCs surface antigens were assayed by flow cytometry. The cells were positive for the MSC-specific cell surface antigens CD73, CD105, and CD90 and negative for the hematopoietic stem cell antigens CD34, CD45, and HLA-DR. (D) Three-directional differentiation of hucMSCs. Adipogenic, osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation were detected by oil red O, Alizarin red, and Alcian blue staining, respectively. Scale bars: 100 μm. (E) Typical characteristics of Exos: transmission electron microscope (TEM) image (left), particle size shown by nano-particle size tracking analysis (NTA) (middle), positive expression of Exos markers including Alix, Tsg 101, and CD63, and negative expression of organelle protein calnexin shown by western blotting (right). Scale bar: 200 nm. Exos: Exosomes; HLA: human leukocyte antigen; hucMSCs: human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.
